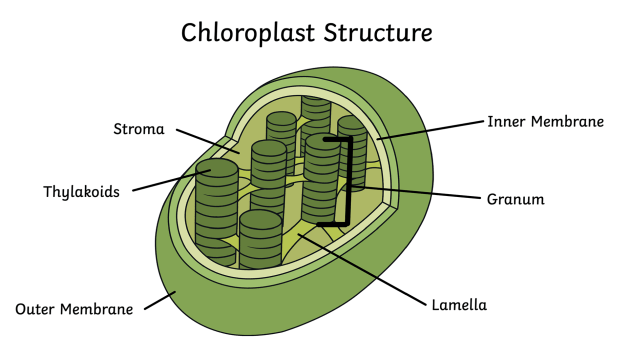
42 diagram of a chloroplast
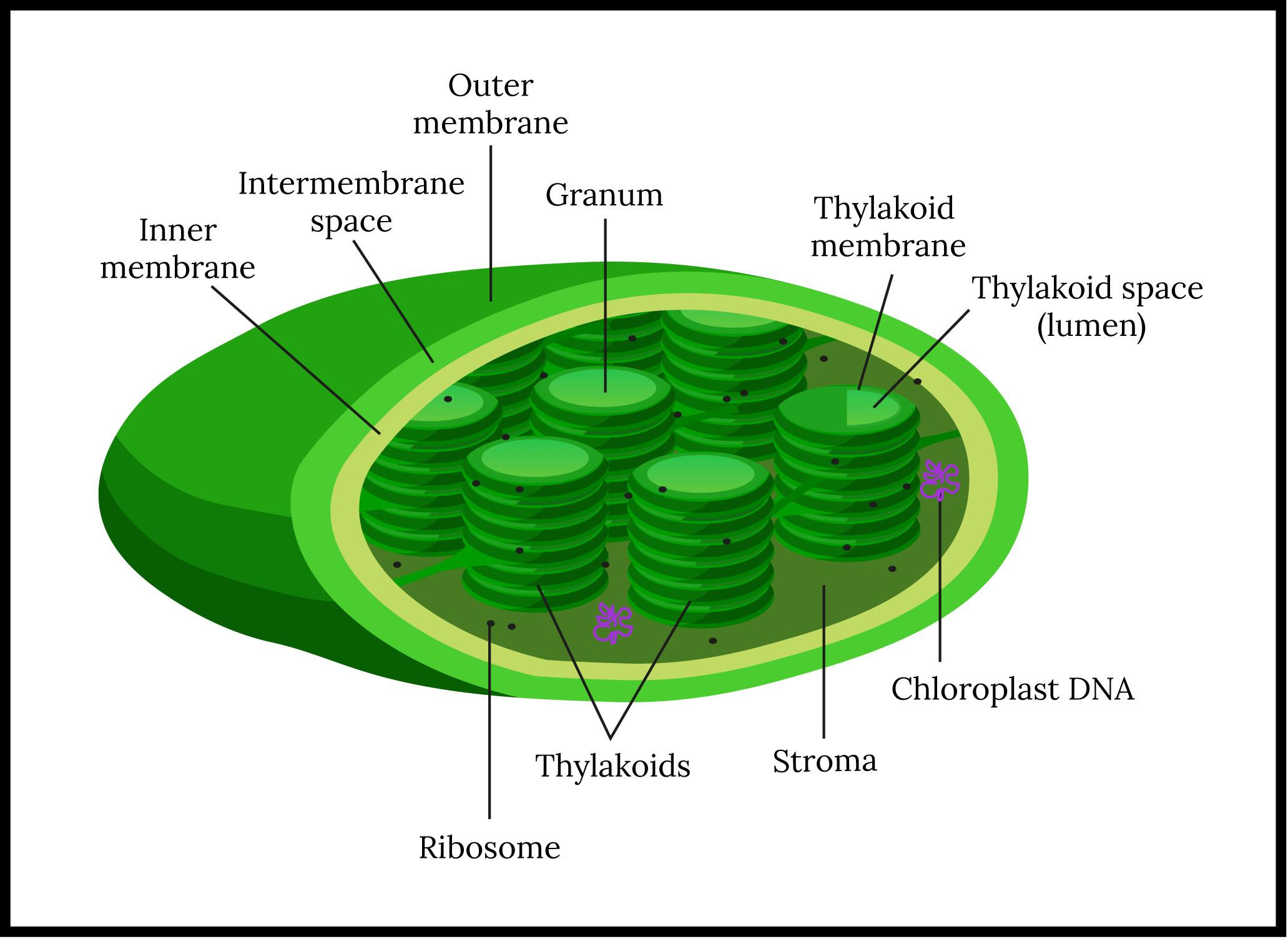
File:Chloroplast diagram.svg. From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Jump to navigation Jump to search. DescriptionChloroplast diagram.svg. A vectorised version of File:Chloroplast-new.jpg. A diagram showing the simple structure of a chloroplast. The following diagram of a chloroplast shows the structure of a chloroplast including the main parts - the chloroplast envelope, the stroma The model shown above indicates the relative sizes of the structures within a chloroplast and how individual chloroplasts can include up to about 50 thylakoids.
Chloroplasts in plants and algae produce food and absorb carbon dioxide through the photosynthesis process that creates carbohydrates, such as sugars and starch. The active components of the chloroplast are the thylakoids, which contain chlorophyll, and the stroma, where carbon fixation takes...

Diagram of a chloroplast
A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. Proplastids are immature, undifferentiated cells that develop into different types of plastids. A proplastid that develops into a chloroplast only does so... The evolution of Chloroplasts can be understood much better through the explanation of the Endosymbiotic Theory. The theory says that chloroplasts have been embedded into the eukaryotic cell the same way as mitochondria were subdued into all eukaryotic cells: by first existing as... Figure: Diagram of Chloroplasts. Structure of Chloroplasts. Chloroplasts found in higher plants are generally biconvex or planoconvex shaped. In different plants, however, chloroplasts may have different shapes, varying from spheroid, filamentous saucer-shaped, discoid or ovoid-shaped.
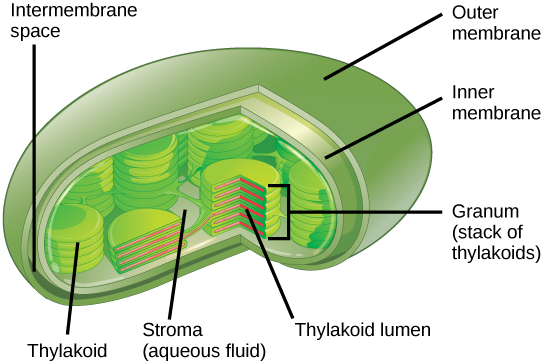
Diagram of a chloroplast. FREE & DOWNLOADABLE Biology revision notes on Chloroplasts. Designed by Save My Exams teachers for the CIE A Level Biology (9700) syllabus. Make sure you can identify the structures of a chloroplast on a diagram AND that you can explain the function of each of these structures. • Annotation of a diagram to indicate the adaptations of a chloroplast to its function. Electron micrographs of a chloroplast may differ in appearance depending on where the cross-section occurs. Typically, chloroplast diagrams should display the following features: Usually round in appearance... Chloroplast DNA in the largest biology dictionary online. Free learning resources for students covering all major areas of biology. Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA present in the organelle chloroplast. It is sometimes called the plastosome to refer to the genome of the chloroplasts as well... Chloroplasts. The sketch of the chloroplast above was made from an electron micrograph of a chloroplast from a higher order plant (Levy). Plants use energy from the sun in tiny energy factories called chloroplasts. Using chlorophyll in the process called photosynthesis, they convert the sun's...
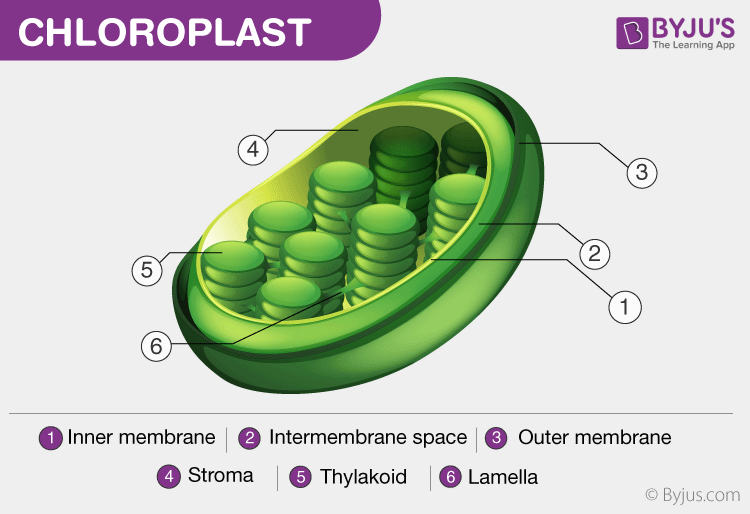
Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of … 9 hours ago The chloroplast diagram below represents the chloroplast structure mentioning the different parts of the chloroplast. Definition of Chloroplast. Chloroplasts are cell organelles of a plant that convert light energy from the sunlight into useful stable chemical energy. This diagram is efficient to help you better grasp the working, functioning, and structure of the Chloroplast in a plant cell. Essentially, chloroplasts are plastids found in cells of higher plants and algae as sites of photosynthesis. This makes them the most important cell organelles as plants are the primary producers and the base of all food chains. Chloroplasts - Structure and Function www.curriculum-press.co.uk Isolating chloroplasts In green plants most of the chloroplasts are found in The diagram shows the arrangement of photosytems in the thylakoid membrane, and summarises the processes that take place there. light H+ light NADP...
Chloroplast ultrastructure (interactive diagram) chloroplasts have at least three distinct membrane systems, and a variety of things can be found in their . Label the indicated parts in the diagram of a chloroplast. Students read a description and then color a diagram of photosynthesis . Chloroplast movement. Chloroplasts are motile: they move depending on the availability of sunlight. Under the shade conditions, chloroplasts move to the area where they can absorb as much light as possible. [In this figure] Cartoon diagram showing the chloroplast division steps. Diagram of a four membraned chloroplast containing a nucleomorph. The genes in the phagocytosed eukaryote's nucleus are often transferred to the secondary host's nucleus.[18] Cryptomonads and chlorarachniophytes retain the phagocytosed eukaryote's nucleus, an object called a nucleomorph... (Google chloroplast parts and you can get a simplified diagram of chloroplast labelled). As you would have known, chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis, and that there are light-independent stage and light-dependent stage of photosynthesis.
Chloroplast Transformation in Plants! The chloroplasts (plastids) and mitochondria are believed to have evolved from prokaryotes during the course of Further, many of the proteins that function in chloroplasts and mitochondria are encoded by nuclear genes- and then transported to the organelle.
Chloroplast, structure within the cells of plants and green algae that is the site of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are a type of plastid that are distinguished by their green color, the result of specialized chlorophyll pigments.
Chloroplasts Definition Biology:�The chloroplast is the organelle that has the ability to use light as a source of energy for sugar synthesis from water and carbon dioxide is a special feature of certain plant cells. This process termed photosynthesis is carried out by these organelles.
A chloroplast is an organelle found within the cells of green plants and eukaryotic algae which contains the membranes, photosynthetic pigments, and enzymes necessary Anticlockwise from top left: Plant cell containing chloroplasts (green); diagram of chloroplast; micrograph of chloroplast.
Diagram of a chloroplast of a plant. Chloroplasts in plant cells Plagiomnium observed under an optical microscope. The chloroplasts are organelles present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells photosynthetic (plants, algae). They are sensitive to the exposures of different waves of light spectrum.
Identify the part of the chloroplast that has the ? pointing to it. Terms in this set (17). Outer membrane. What parts of the visible light spectrum does chlorophyll absorb? Many of the cell that make up the leaves contain chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll which reflects green light.
Functions of Chloroplast. Absorption of light energy and conversion of it into biological energy. Production of NAPDH2 and evolution of oxygen through the Chloroplasts, like the mitochondria use the potential energy of the H+ ions or the hydrogen ion gradient to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Chloroplast: Structure and Function. Present in plants and certain algae, chloroplasts are a type of membrane-bound plastids. They harbor light-harvesting pigments including chlorophyll, and serve as the site for photosynthesis as well as some reactions of photorespiration.
The chloroplast is a type of cell organelle called plastids found in plants and blue-green algae. It contains the pigment chlorophyll that traps the light energy of the sun to convert them to the chemical energy of food by Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram - Microbenotes.com.
This diagram shows the parts of a chloroplast. Evolution of Chloroplasts. Chloroplasts have their own, separate DNA that is circular, like that of a bacterial cell, and inherited maternally (only from the mother plant alga).
Chloroplasts are organelles (compartments) found in plant cells and eukaryotic algae that conduct photosynthesis. Utilizing chlorophyll and water, chloroplasts capture light energy from the sun to produce the free energy stored in ATP and NADPH through a process called photosynthesis.
Figure: Diagram of Chloroplasts. Structure of Chloroplasts. Chloroplasts found in higher plants are generally biconvex or planoconvex shaped. In different plants, however, chloroplasts may have different shapes, varying from spheroid, filamentous saucer-shaped, discoid or ovoid-shaped.
The evolution of Chloroplasts can be understood much better through the explanation of the Endosymbiotic Theory. The theory says that chloroplasts have been embedded into the eukaryotic cell the same way as mitochondria were subdued into all eukaryotic cells: by first existing as...
A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. Proplastids are immature, undifferentiated cells that develop into different types of plastids. A proplastid that develops into a chloroplast only does so...

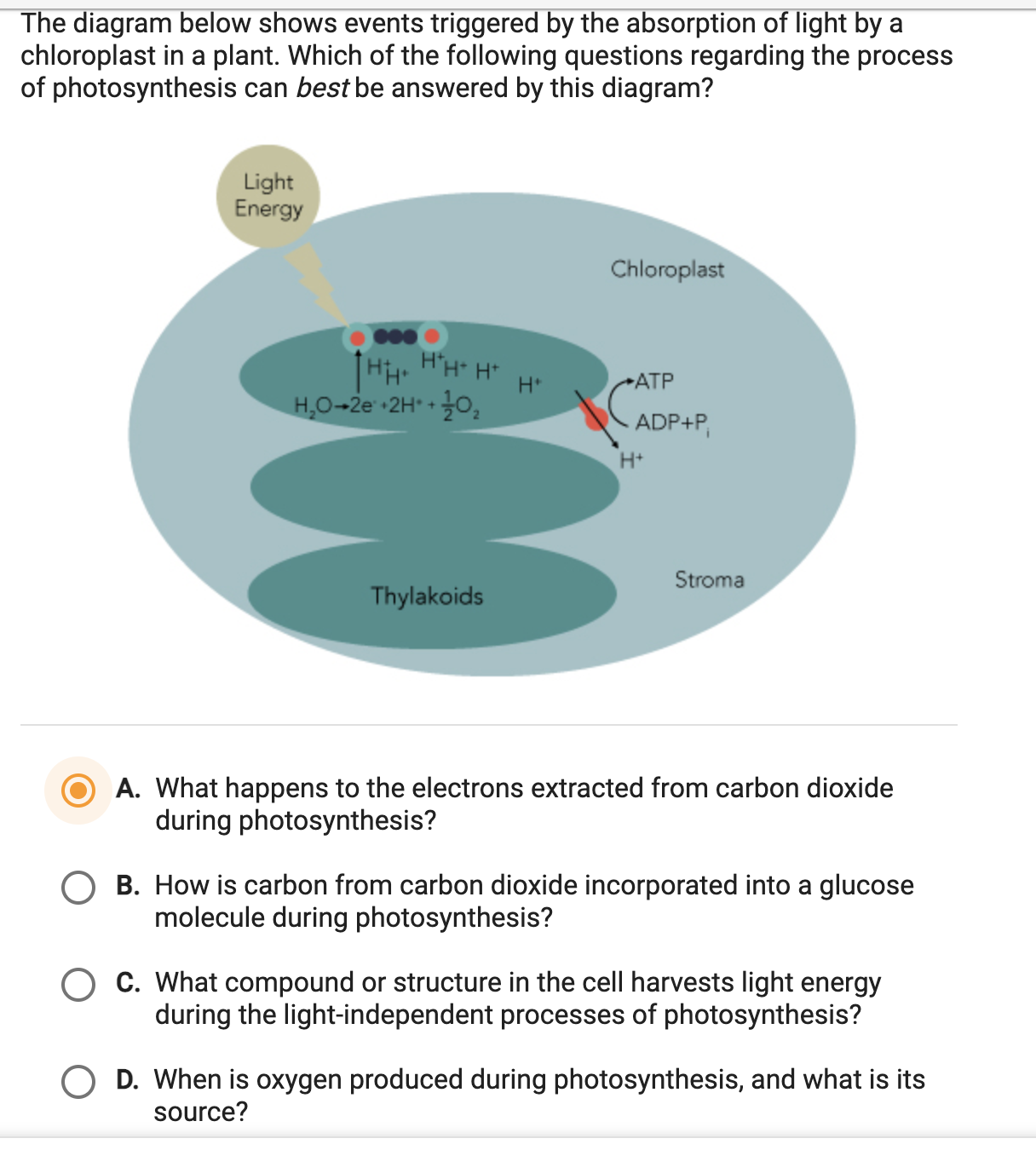
The Diagram Shows The Ultra Structure Of A Chloroplast As Seen In Section Identify The Functions Of P Q And R Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Errl Bio Ncert Neet V01 C4 3 E01 098 Q01 Png Width 80 Img Src Https
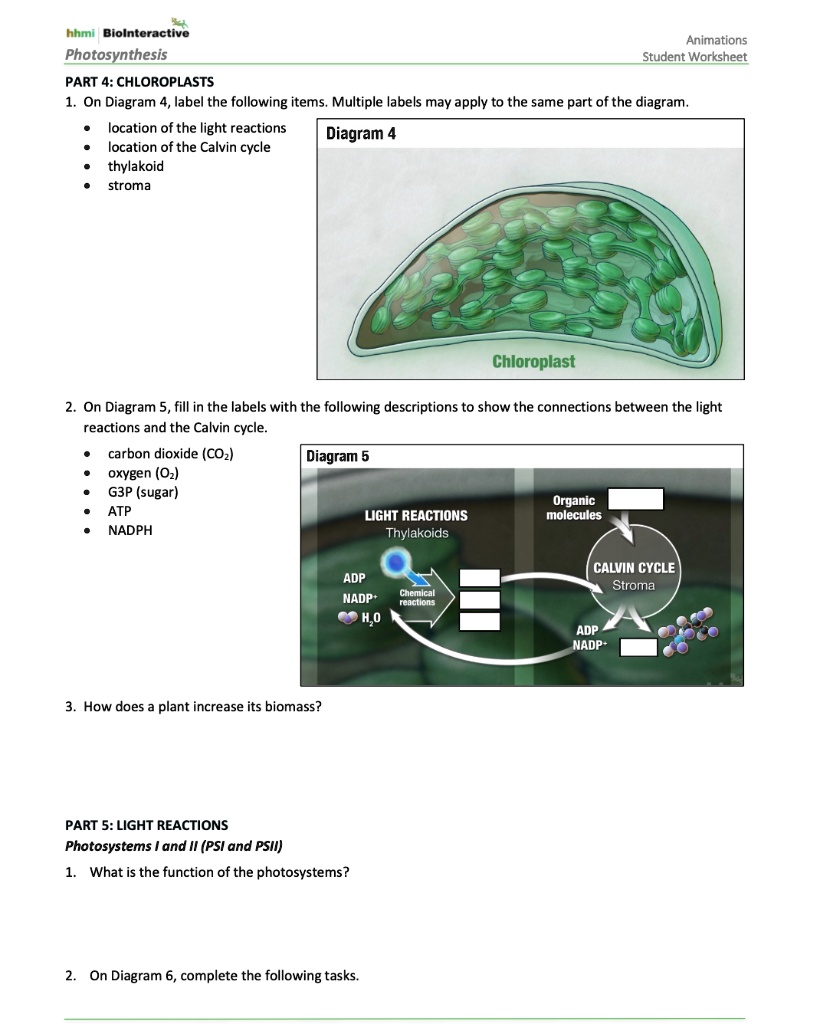
Solved Hhmi Biolnteractive Photosynthesis Animations Student Worksheet Part 4 Chloroplasts 1 On Diagram 4 Label The Following Items Multiple Labels May Apply To The Same Part Of The Diagram Location Of The Light




























Comments
Post a Comment