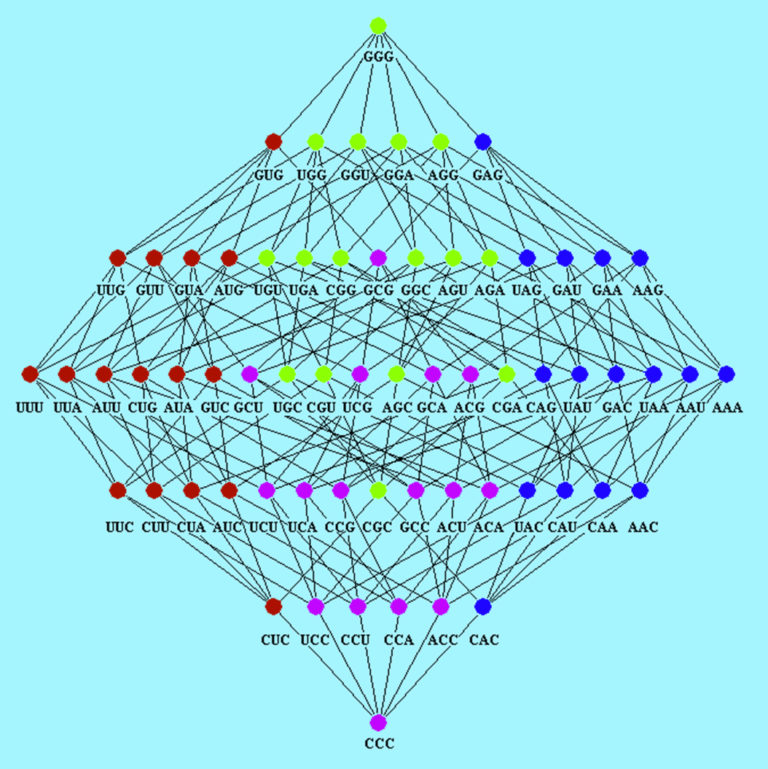
42 hasse diagram examples
Bottom elements of the Hasse Diagram. Example- In the diagram above, we can say that 1 is related to 2,3,4,6,12 (ordered by division e.g. (4,/) ) but no element is related to 1. (As Hasse Diagram is upward directional). Greatest element (if it exists) is the element succeeding all other elements. The Hasse diagram is much simpler than the directed graph of the partial order. Example: Consider the set A = {4, 5, 6, 7}. Let R be the relation ≤ on A. Draw the directed graph and the Hasse diagram of R. Solution: The relation ≤ on the set A is given by. R = {{4, 5}, {4, 6}, {4, 7}, {5, 6}, {5, 7}, {6, 7}, {4, 4}, {5, 5}, {6, 6}, {7, 7}} The directed graph of the relation R is as shown in fig: To draw the Hasse diagram of partial order, apply the following points: Delete all edges ...
A Hasse diagram is a graphical representation of the relation of elements of a partially ordered set (poset) with an implied upward orientation.A point is drawn for each element of the partially ordered set (poset) and joined with the line segment according to the following rules: If p

Hasse diagram examples
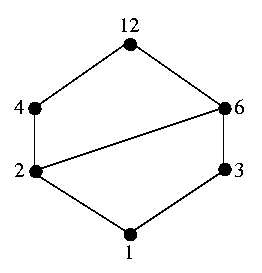
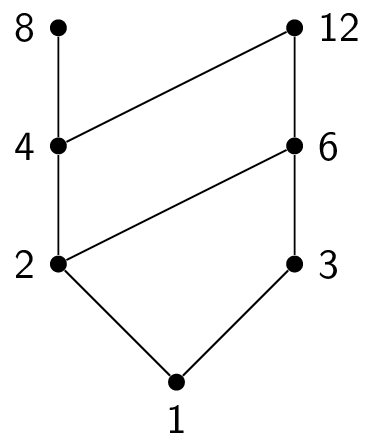
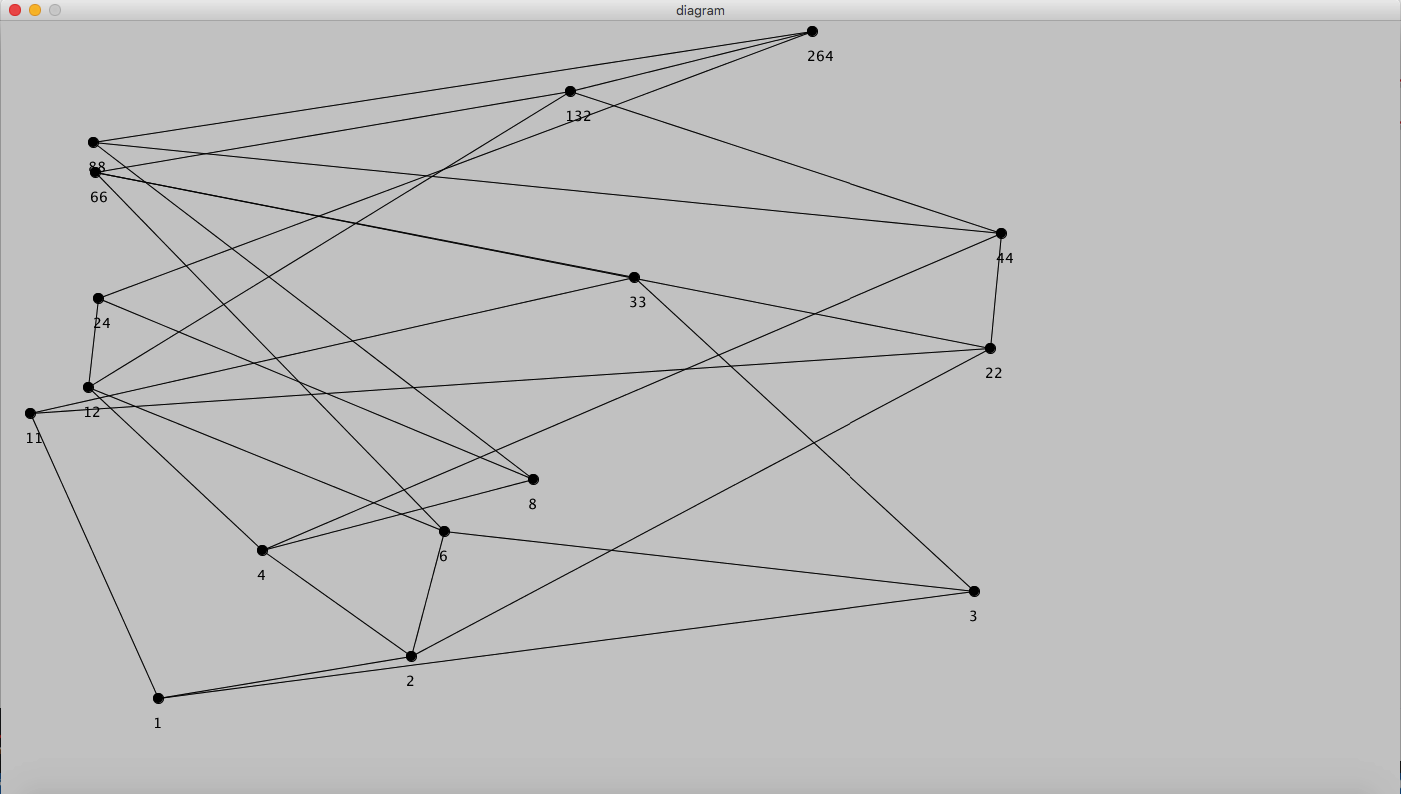
For example, suppose we are given the following partial ordering, indicated in the Hasse diagram below, and subset S = {10,15}. Then the least upper bound of 10 and 15 is 30, which is the least common multiple, and the place where 10 "joins" 15. Hasse diagrams are meant to present partial order relations in equivalent but somewhat simpler forms by removing certain deducible ''noncritical'' parts of the relations. For better motivation and understanding, we'll introduce it through the following examples. Examples. The relation in example 2 can be drawn as Jan 10, 2022 · Determine the Hasse diagram for it and two upper bounds. 0. Number of Hasse diagrams of a lattice with less or equal to n elements. 1. Formal Definition of a … Draw the Hasse diagram representing the divisibility relation on set Solution. We place at the bottom of the diagram and on the next level.
Hasse diagram examples. For example, the poset would be converted to a Hasse diagram like - The last figure in the above diagram contains sufficient information to find the partial ordering. This diagram is called a Hasse Diagram. Extremums in Posets : Elements of posets that have certain extremal properties are important for many applications. Return the (normalized) rank function of the poset, if it exists. A rank function of a poset P is a function r that maps elements of P to integers and satisfies: r(x) = r(y) + 1 if x covers y. The function r is normalized such that its minimum value on every connected component of the Hasse diagram of P is 0. edges upward are left implicit instead of cluttering up the diagram. These graphs are called Hasse diagrams after the twentieth-century German number theorist Helmut Hasse. z EXAMPLE 7.1-4 Diagram the following posets: a) The poset of Example 3b: the divisors of 36 ordered by m|n. b) The poset P(S) for S = {0,1,2}, ordered by R ⊆ T. Solution Remove directions on edges assuming that they are oriented upwards. So if then the vertex appears above the vertex. The resulting graph looks far simpler and is called a Hasse diagram, named after the German mathematician Helmut Hasse. Fig.1 Helmut Hasse (1898-1979) As an example, consider the divisibility relation on the set.
A Hasse Diagram basically looks like a bunch of nodes, an TikZ is very good at drawing bunches of nodes. These examples should help you to get going. - romeovs Example 7 – Constructing a Hasse Diagram Consider the “subset” relation, ⊆, on the set ({a, b, c}). That is, for all sets U and V in ({a, b, c}), Construct the Hasse diagram for this relation. Solution: Draw the directed graph of the relation in such a way that all arrows except loops point upward. Hasse Diagrams: Example (1) • Of course, you need not always start with the complete relation in the partial order and then trim everything. • Rather, you can build a Hasse Diagram directly from the partial order • Example: Draw the Hasse Diagram Hasse Diagram is created for POSET or Partially Ordered Set. It means that there is a set of elements in which certain element are ordered, sequenced or ...
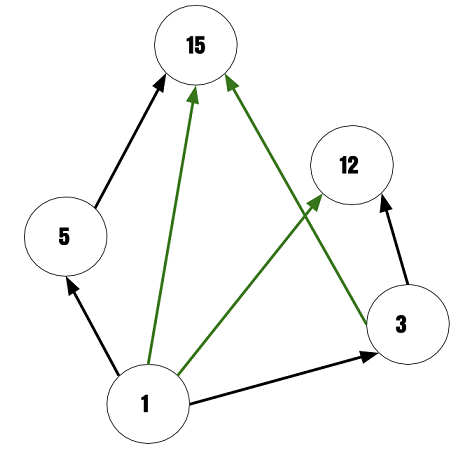
1. The Hasse Diagram Hasse diagram is a graphical orientation of a finite partially ordered set, also known as POSETs. Dots denote the elements present in the POSETs, whereas straight lines express their relationship. The hasse diagrams are relevant for studying the set and theories related to it and representing Boolean Algebra.. Although the initial representation of the hasse diagram ... Rules for Hasse Diagram. 1. If x < y, then in the graph x appears lower to y. 2. We draw line segment between x and y only if x cover y or y cover x, it means some order is maintained between them. Consider an example. Let A be a set, A = { 1, 3, 5, 12, 15 }, relation between elements are a | b that is., a divides b. Poset Diagram(Hasse diagram): Let [A;R] be a poset. The poset diagram is as follows I. There is a vertex corresponding to each element of 'A'. II. An edge between the elements 'a' and 'b' is not present in the diagram if there exists an element x∈ A such that aRx and xRb. III. Hasse Diagram. The best way to graphically understand and represent partial orders is via a Hasse Diagram. A Hasse diagram is a graph for a partial ordering that does not have loops or arcs that imply transitivity and is drawn upward, thus, eliminating the need for directional arrows. How To Draw A Hasse Diagram
For example, consider the poset $(\{1,2,3,4\}, \le)$. We start with all information. We now remove all self-loops: We then remove the edges required for transitivity: We now remove the arrows by placing all of the initial elements below the terminal elements: This is the Hasse diagram. Here are some more examples of Hasse diagrams:

Finance investment stock market chart. Made with analog vintage lens, Leica APO Macro Elmarit-R 2.8 100mm (Year: 1993)
Examples. The partial order P whose Hasse diagram is illustrated in Figure 5.13 has dimension 2. A minimum realizer for P is also shown.
PLZ LIKE SHARE AND SUBSCRIBE
This video explain step-by-step procedure to draw a Hasse Diagram of a given POSET with the help of an example._____You c...
The corresponding Hasse diagram is shown in. Fig.1. For the pairs of elements (2, 3) and (3, 5), there is. no upper bound. Hence, the least upper bound. does not exist. This implies that ( {1, 2 ...
Example 2 Let Cancer constellation represent the Hasse diagram of a partial order relation. List the ordered pairs of the relation and find its binary matrix. Example 3 Let and Show that the relation is a partial order and draw its Hasse diagram. Example 4 Draw the Hasse diagram representing the divisibility relation on set Example 5
Example: In the above Hasse diagram, ∅ is a minimal element and {a, b, c} is a maximal element. Least and Greatest Elements Definition: Let (A, R) be a poset. Then a in A is the least element if for every element b in A , aRb and b is the greatest element if for every element a in A , aRb .
In order theory, a Hasse diagram (/ ˈ h æ s ə /; German: ) is a type of mathematical diagram used to represent a finite partially ordered set, in the form of a drawing of its transitive reduction.Concretely, for a partially ordered set (S, ≤) one represents each element of S as a vertex in the plane and draws a line segment or curve that goes upward from x to y whenever y covers x (that ...
A poset can be visualized through its Hasse diagram, which depicts the ordering relation. Partial order relation. A partial order relation is a homogeneous relation that is transitive and antisymmetric. There are two common sub-definitions for a partial order relation, for reflexive and irreflexive partial order relations, also called "non ...
A Hasse diagram is a graphical rendering of a partially ordered set displayed via the cover relation of the partially ordered set with an implied upward orientation. A point is drawn for each element of the poset , and line segments are drawn between these points according to the following two rules: 1.
Example: Consider the following poset represented by the following Hasse diagram In this poset, a, f and i are minimal elements c, h, k are maximal elements, there is a no greatest element and there is no least element. Consider the following posets represented by Hasse diagrams.
The Hasse diagram below represents the partition lattice on a set of elements. What is distributive lattice with example? In mathematics, a distributive lattice is a lattice in which the operations of join and meet distribute over each other.
EXAMPLE • Let A={1,2,3,4,12}. Consider the partial order of divisibility on A. Draw the corresponding Hasse diagram. 5 12 4 2 1 3 12 4 2 1 3 6. Shirt innerwear Tie Jacket Trouser Belt HASSE DIAGRAM Left Sock Right Sock Left Shoe Right Shoe 7.
The Hasse diagram of a poset is a simpler version of the digraph representing the partial order relation. The properties of a partial order assure us that its digraph can be drawn in an oriented plane so that each element lies below all other elements ... Example 4.10.1. The Hasse diagram for (P({a,b,c}),⊆) is {a,b,c}
Hasse Diagrams •Since partial orderings is a binary relation, it can be represented by a directed graph •However, many edges can be omitted, because such an ordering must be reflexive and transitive •Also, we may order the vertices in the graph in a 'vertical' manner, such that all edges are pointing from low to high
Jan 10, 2022 · Determine the Hasse diagram for it and two upper bounds. 0. Number of Hasse diagrams of a lattice with less or equal to n elements. 1. Formal Definition of a … Draw the Hasse diagram representing the divisibility relation on set Solution. We place at the bottom of the diagram and on the next level.
Hasse diagrams are meant to present partial order relations in equivalent but somewhat simpler forms by removing certain deducible ''noncritical'' parts of the relations. For better motivation and understanding, we'll introduce it through the following examples. Examples. The relation in example 2 can be drawn as
For example, suppose we are given the following partial ordering, indicated in the Hasse diagram below, and subset S = {10,15}. Then the least upper bound of 10 and 15 is 30, which is the least common multiple, and the place where 10 "joins" 15.

Hasse diagram examples
For example, suppose we are given the following partial ordering, indicated in the Hasse diagram below, and subset S = {10,15}. Then the least upper bound of 10 and 15 is 30, which is the least common multiple, and the place where 10 "joins" 15. Hasse diagrams are meant to present partial order relations in equivalent but somewhat simpler forms by removing certain deducible ''noncritical'' parts of the relations. For better motivation and understanding, we'll introduce it through the following examples. Examples. The relation in example 2 can be drawn as Jan 10, 2022 · Determine the Hasse diagram for it and two upper bounds. 0. Number of Hasse diagrams of a lattice with less or equal to n elements. 1. Formal Definition of a … Draw the Hasse diagram representing the divisibility relation on set Solution. We place at the bottom of the diagram and on the next level.
Hasse diagram examples. For example, the poset would be converted to a Hasse diagram like - The last figure in the above diagram contains sufficient information to find the partial ordering. This diagram is called a Hasse Diagram. Extremums in Posets : Elements of posets that have certain extremal properties are important for many applications. Return the (normalized) rank function of the poset, if it exists. A rank function of a poset P is a function r that maps elements of P to integers and satisfies: r(x) = r(y) + 1 if x covers y. The function r is normalized such that its minimum value on every connected component of the Hasse diagram of P is 0. edges upward are left implicit instead of cluttering up the diagram. These graphs are called Hasse diagrams after the twentieth-century German number theorist Helmut Hasse. z EXAMPLE 7.1-4 Diagram the following posets: a) The poset of Example 3b: the divisors of 36 ordered by m|n. b) The poset P(S) for S = {0,1,2}, ordered by R ⊆ T. Solution Remove directions on edges assuming that they are oriented upwards. So if then the vertex appears above the vertex. The resulting graph looks far simpler and is called a Hasse diagram, named after the German mathematician Helmut Hasse. Fig.1 Helmut Hasse (1898-1979) As an example, consider the divisibility relation on the set.
A Hasse Diagram basically looks like a bunch of nodes, an TikZ is very good at drawing bunches of nodes. These examples should help you to get going. - romeovs Example 7 – Constructing a Hasse Diagram Consider the “subset” relation, ⊆, on the set ({a, b, c}). That is, for all sets U and V in ({a, b, c}), Construct the Hasse diagram for this relation. Solution: Draw the directed graph of the relation in such a way that all arrows except loops point upward. Hasse Diagrams: Example (1) • Of course, you need not always start with the complete relation in the partial order and then trim everything. • Rather, you can build a Hasse Diagram directly from the partial order • Example: Draw the Hasse Diagram Hasse Diagram is created for POSET or Partially Ordered Set. It means that there is a set of elements in which certain element are ordered, sequenced or ...
1. The Hasse Diagram Hasse diagram is a graphical orientation of a finite partially ordered set, also known as POSETs. Dots denote the elements present in the POSETs, whereas straight lines express their relationship. The hasse diagrams are relevant for studying the set and theories related to it and representing Boolean Algebra.. Although the initial representation of the hasse diagram ... Rules for Hasse Diagram. 1. If x < y, then in the graph x appears lower to y. 2. We draw line segment between x and y only if x cover y or y cover x, it means some order is maintained between them. Consider an example. Let A be a set, A = { 1, 3, 5, 12, 15 }, relation between elements are a | b that is., a divides b. Poset Diagram(Hasse diagram): Let [A;R] be a poset. The poset diagram is as follows I. There is a vertex corresponding to each element of 'A'. II. An edge between the elements 'a' and 'b' is not present in the diagram if there exists an element x∈ A such that aRx and xRb. III. Hasse Diagram. The best way to graphically understand and represent partial orders is via a Hasse Diagram. A Hasse diagram is a graph for a partial ordering that does not have loops or arcs that imply transitivity and is drawn upward, thus, eliminating the need for directional arrows. How To Draw A Hasse Diagram
For example, consider the poset $(\{1,2,3,4\}, \le)$. We start with all information. We now remove all self-loops: We then remove the edges required for transitivity: We now remove the arrows by placing all of the initial elements below the terminal elements: This is the Hasse diagram. Here are some more examples of Hasse diagrams:

Finance investment stock market chart. Made with analog vintage lens, Leica APO Macro Elmarit-R 2.8 100mm (Year: 1993)
Examples. The partial order P whose Hasse diagram is illustrated in Figure 5.13 has dimension 2. A minimum realizer for P is also shown.
PLZ LIKE SHARE AND SUBSCRIBE
This video explain step-by-step procedure to draw a Hasse Diagram of a given POSET with the help of an example._____You c...
The corresponding Hasse diagram is shown in. Fig.1. For the pairs of elements (2, 3) and (3, 5), there is. no upper bound. Hence, the least upper bound. does not exist. This implies that ( {1, 2 ...
Example 2 Let Cancer constellation represent the Hasse diagram of a partial order relation. List the ordered pairs of the relation and find its binary matrix. Example 3 Let and Show that the relation is a partial order and draw its Hasse diagram. Example 4 Draw the Hasse diagram representing the divisibility relation on set Example 5
Example: In the above Hasse diagram, ∅ is a minimal element and {a, b, c} is a maximal element. Least and Greatest Elements Definition: Let (A, R) be a poset. Then a in A is the least element if for every element b in A , aRb and b is the greatest element if for every element a in A , aRb .
In order theory, a Hasse diagram (/ ˈ h æ s ə /; German: ) is a type of mathematical diagram used to represent a finite partially ordered set, in the form of a drawing of its transitive reduction.Concretely, for a partially ordered set (S, ≤) one represents each element of S as a vertex in the plane and draws a line segment or curve that goes upward from x to y whenever y covers x (that ...
A poset can be visualized through its Hasse diagram, which depicts the ordering relation. Partial order relation. A partial order relation is a homogeneous relation that is transitive and antisymmetric. There are two common sub-definitions for a partial order relation, for reflexive and irreflexive partial order relations, also called "non ...
A Hasse diagram is a graphical rendering of a partially ordered set displayed via the cover relation of the partially ordered set with an implied upward orientation. A point is drawn for each element of the poset , and line segments are drawn between these points according to the following two rules: 1.
Example: Consider the following poset represented by the following Hasse diagram In this poset, a, f and i are minimal elements c, h, k are maximal elements, there is a no greatest element and there is no least element. Consider the following posets represented by Hasse diagrams.
The Hasse diagram below represents the partition lattice on a set of elements. What is distributive lattice with example? In mathematics, a distributive lattice is a lattice in which the operations of join and meet distribute over each other.
EXAMPLE • Let A={1,2,3,4,12}. Consider the partial order of divisibility on A. Draw the corresponding Hasse diagram. 5 12 4 2 1 3 12 4 2 1 3 6. Shirt innerwear Tie Jacket Trouser Belt HASSE DIAGRAM Left Sock Right Sock Left Shoe Right Shoe 7.
The Hasse diagram of a poset is a simpler version of the digraph representing the partial order relation. The properties of a partial order assure us that its digraph can be drawn in an oriented plane so that each element lies below all other elements ... Example 4.10.1. The Hasse diagram for (P({a,b,c}),⊆) is {a,b,c}
Hasse Diagrams •Since partial orderings is a binary relation, it can be represented by a directed graph •However, many edges can be omitted, because such an ordering must be reflexive and transitive •Also, we may order the vertices in the graph in a 'vertical' manner, such that all edges are pointing from low to high
Jan 10, 2022 · Determine the Hasse diagram for it and two upper bounds. 0. Number of Hasse diagrams of a lattice with less or equal to n elements. 1. Formal Definition of a … Draw the Hasse diagram representing the divisibility relation on set Solution. We place at the bottom of the diagram and on the next level.
Hasse diagrams are meant to present partial order relations in equivalent but somewhat simpler forms by removing certain deducible ''noncritical'' parts of the relations. For better motivation and understanding, we'll introduce it through the following examples. Examples. The relation in example 2 can be drawn as
For example, suppose we are given the following partial ordering, indicated in the Hasse diagram below, and subset S = {10,15}. Then the least upper bound of 10 and 15 is 30, which is the least common multiple, and the place where 10 "joins" 15.






![95 [PDF] SEQUENCE DIAGRAM EXAMPLE YOUTUBE PRINTABLE ...](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/proxy/AVvXsEh10QCEToOfxIBRNLrSz2D4-ZJqNex1cqfJk84o9gW7B8T3nacb4ytMWIaE_Z6XSP9IJi3myLbGw8w30MbnINRF-F6TTayAP5c4rYAu2VakZySKp2tiZxFKtKWQWKiTNpDZewdt6_LxCHc4zhIghT_5iA6PQ4vyBMVIF3BiZ7J8kjh9Qrw4NBDbTe342rFNWtAClX4EeNc5sVKM6uxD=s0-d)












Comments
Post a Comment