43 free body diagram khan academy
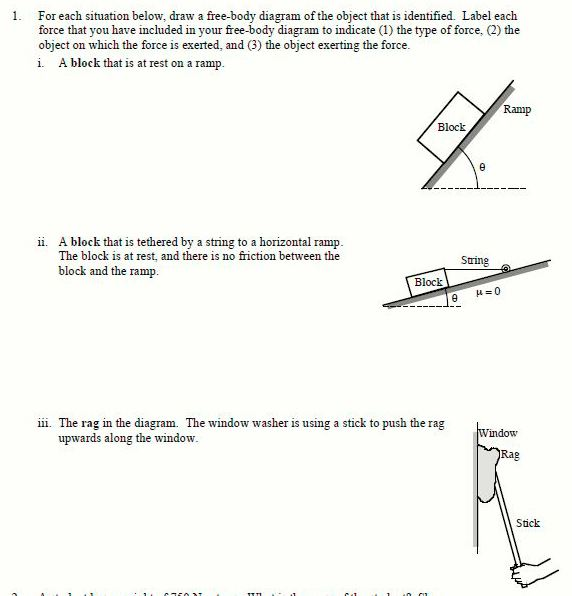
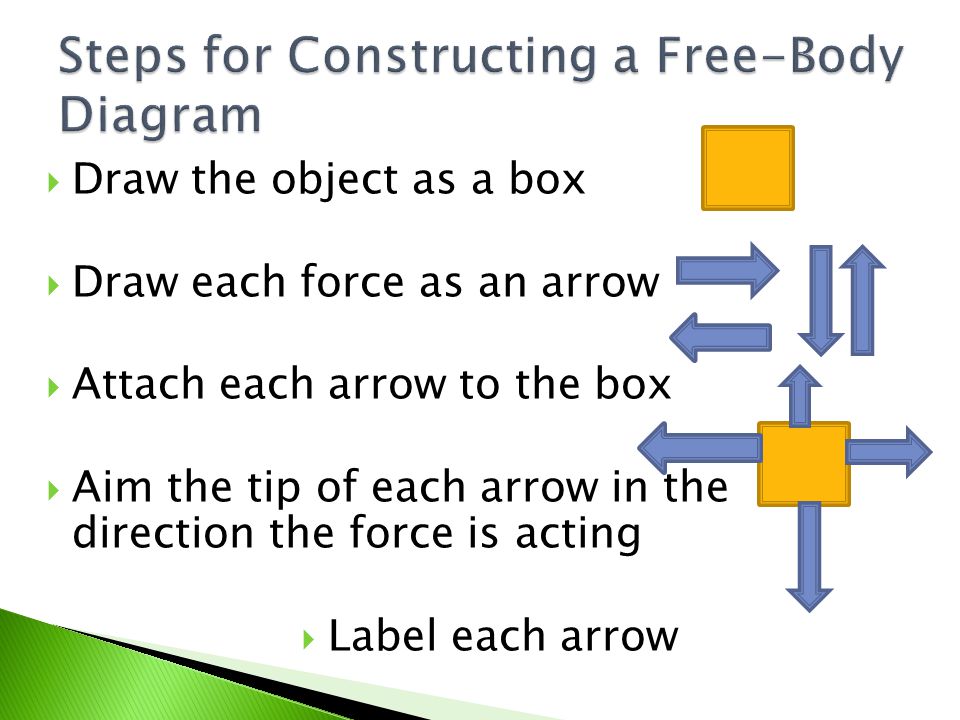
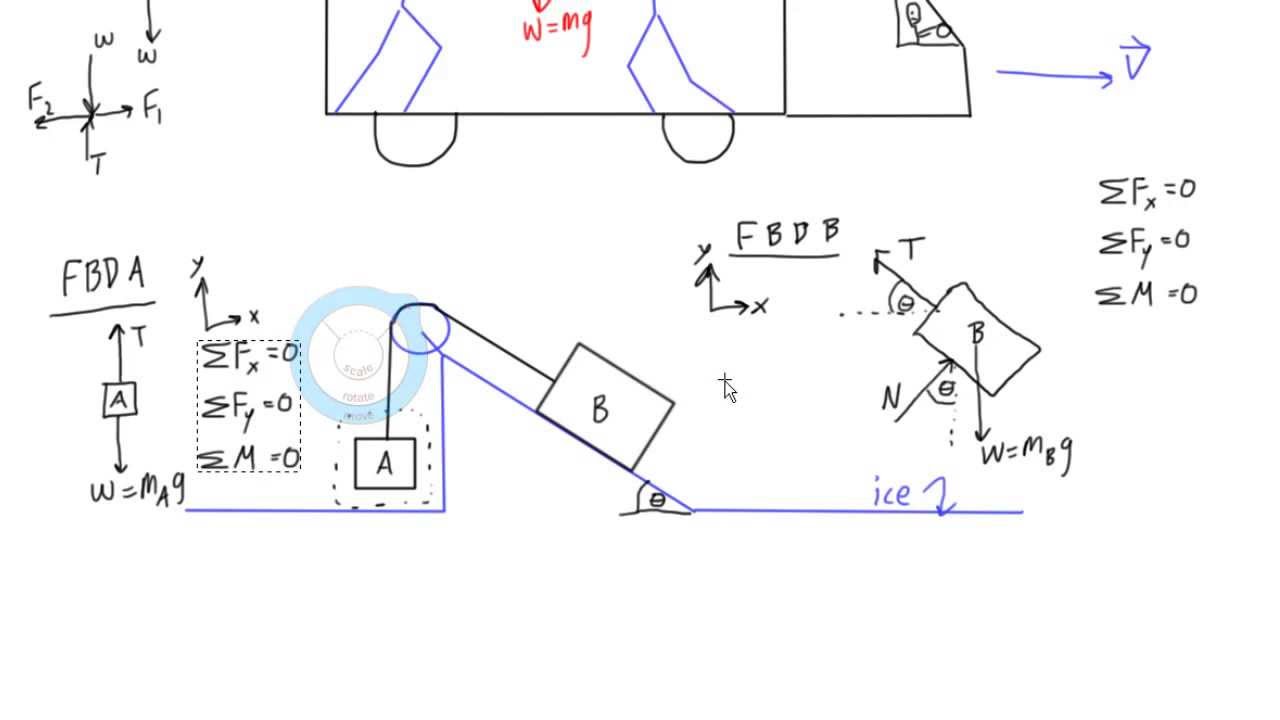
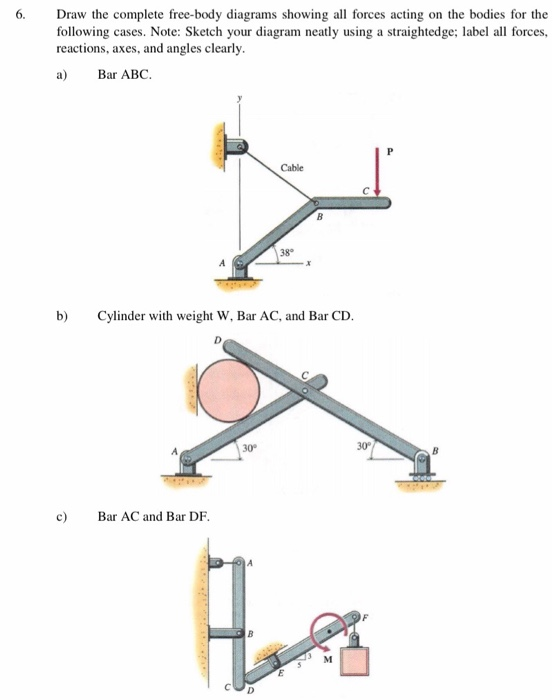
Equations of equilibrium, Free body diagram, Reaction, Static indeterminacy and partial constraints, Two and three force systems. Structures : 2D truss, Method of joints, Method of section. Frame, Beam, types of loading and supports, Shear Force and Bending Moment diagram, relation among load-shear force-bending moment. FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape. 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) the weight of the body, and c) support reactions (can be difficult).
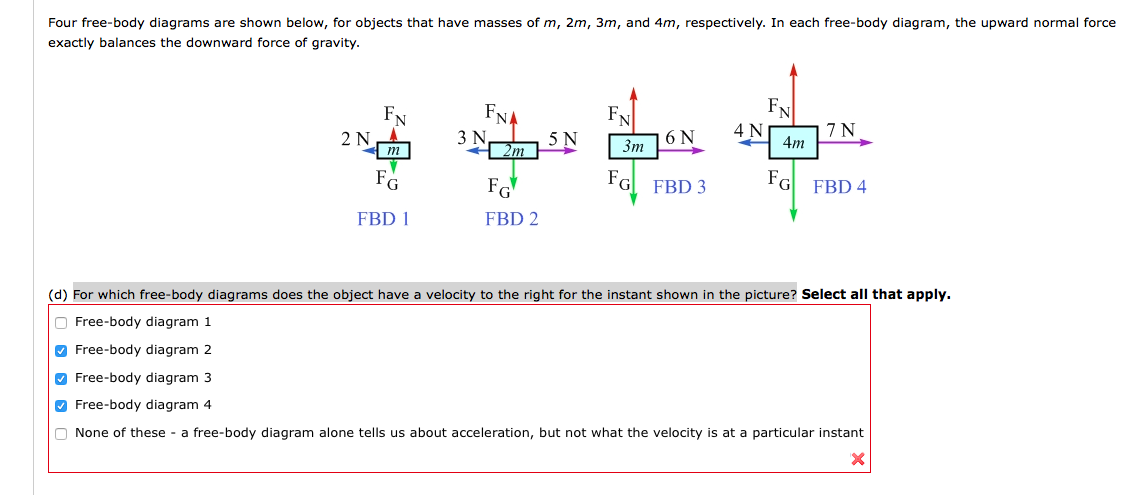
nent of velocity and that The free-body diagram is shown in Fig. T1.1b. Newton's second law gives and the components of acceleration including the effects of both gravity and air drag are (T1.2) The constant D depends on the density of air, the silhouette area A of the body (its area as seen from the front), and a dimensionless constant C ...
Free body diagram khan academy
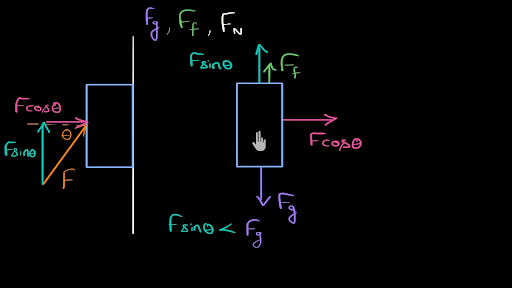
All About Vectors - website (physicsclassroom.com) - read Lessons 1 & 3 (see the Khan Academy video below for help with Lesson 3) Force Vectors (and the meaning of a vector's sense) - website (mit.edu) Free Body Diagrams (FBDs) - website (physicsclassroom.com) Drawing Free Body Diagrams - YouTube video1 and video2 (Bozeman Science). Solving for Forces Using a FBD (static case) - YouTube video ... Sal draws a free body diagram for a box held stationary against a wall with a force at an angle theta.View more lessons or practice this subject at https://w... Three times five is 15. Subtract, I get a two here, bring down the zero. Five goes into 20 four times. Four times five is 20, and it works out perfectly. So each of these five-fourths are 34 meters. 34 meters, 34 meters, 34 meters, 34 meters, and 34 meters.
Free body diagram khan academy. The free-body diagram is used to identify the unknown forces acting on the object when applying the equilibrium equation (1.1) to the object. The procedure for solving equilibrium problems is therefore as follows: 1. Draw a free-body diagram—you must choose an object to isolate that results in a free-body diagram including Details. This Demonstration shows a free-body diagram of an object as it is just about to tip over (impending motion). In that case, the normal force acts at the far right instead of along the centerline of the object. Friction acts at the base of the object in a direction opposing the motion of the object and along the surface. Free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion (practice) | Khan Academy Check your understanding of free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion in this set of free practice questions aligned to AP Physics I standards. Physics Classroom Free Body Diagram Practice: updated with all answers! Free Page 1/11. Download File PDF Body Diagram Practice And AnswersBody Diagrams Examples (Worksheet ... Along Types of forces and free body diagrams | AP Physics 1 | Khan Academy Page 2/11. Download File PDF Body Diagram Practice And Answers12.1 Pulley Problems Weekly Hashkafa
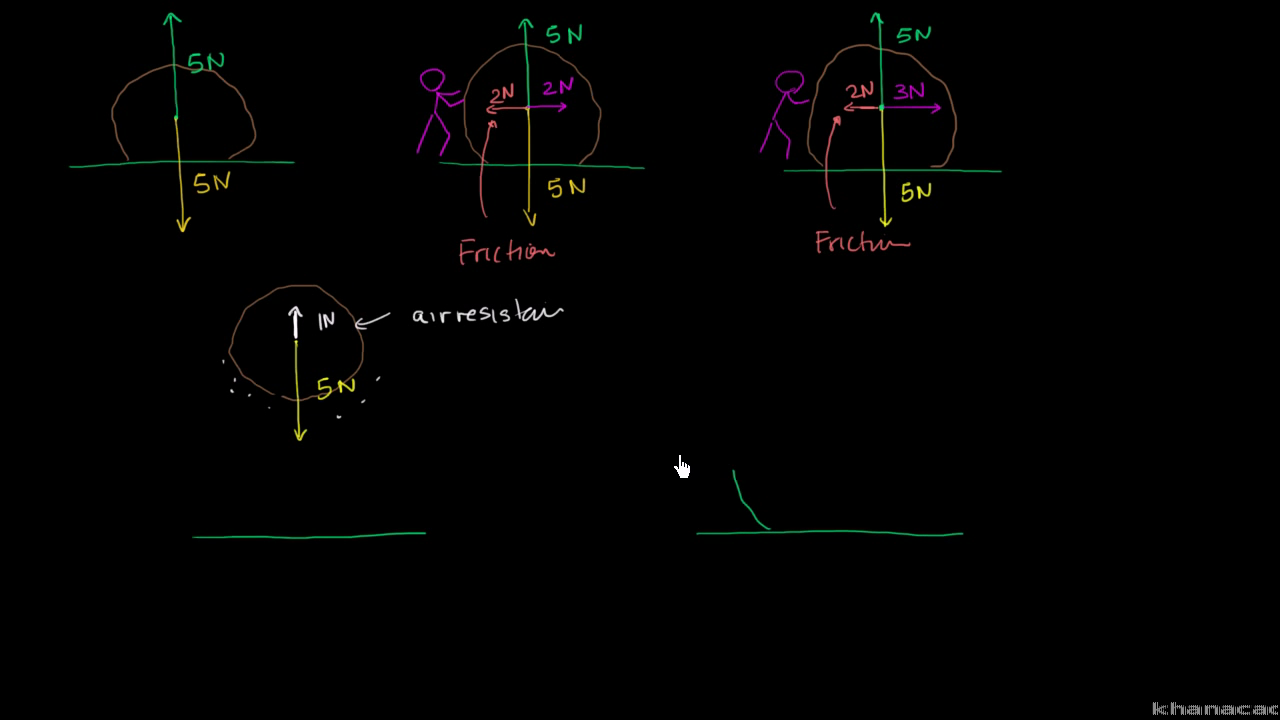
Introduction to forces and free body diagrams review Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. Include the force, include the force of gravity acting on this block. Include the force of friction acting on this block and include the normal force of the wall acting on the block as well. Pause the video and try to have a go at it. So before I even start to draw the free body diagram, let's break down this force into its vertical and ... body diagrams | AP Physics 1 | Khan Academy Tension force in strings (Easy method + Numerical) - two mass in an elevator | Newton's laws Body Parts - Science Lesson for Preschoolers Free Body Diagrams - Tension, Friction, Inclined A look at the pelvic organs of the female reproductive system.
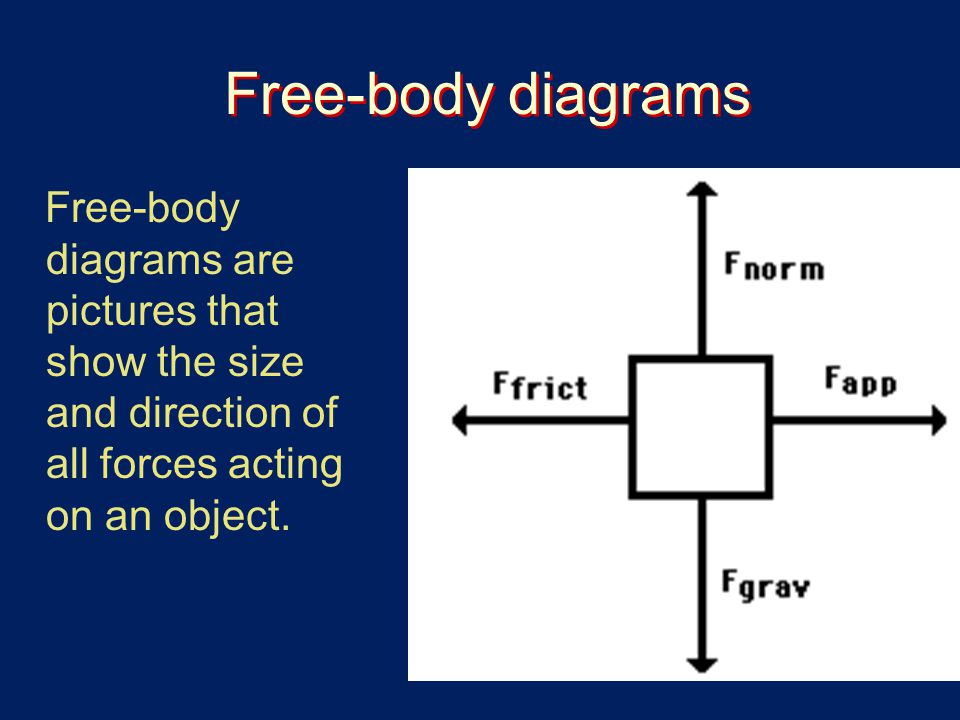
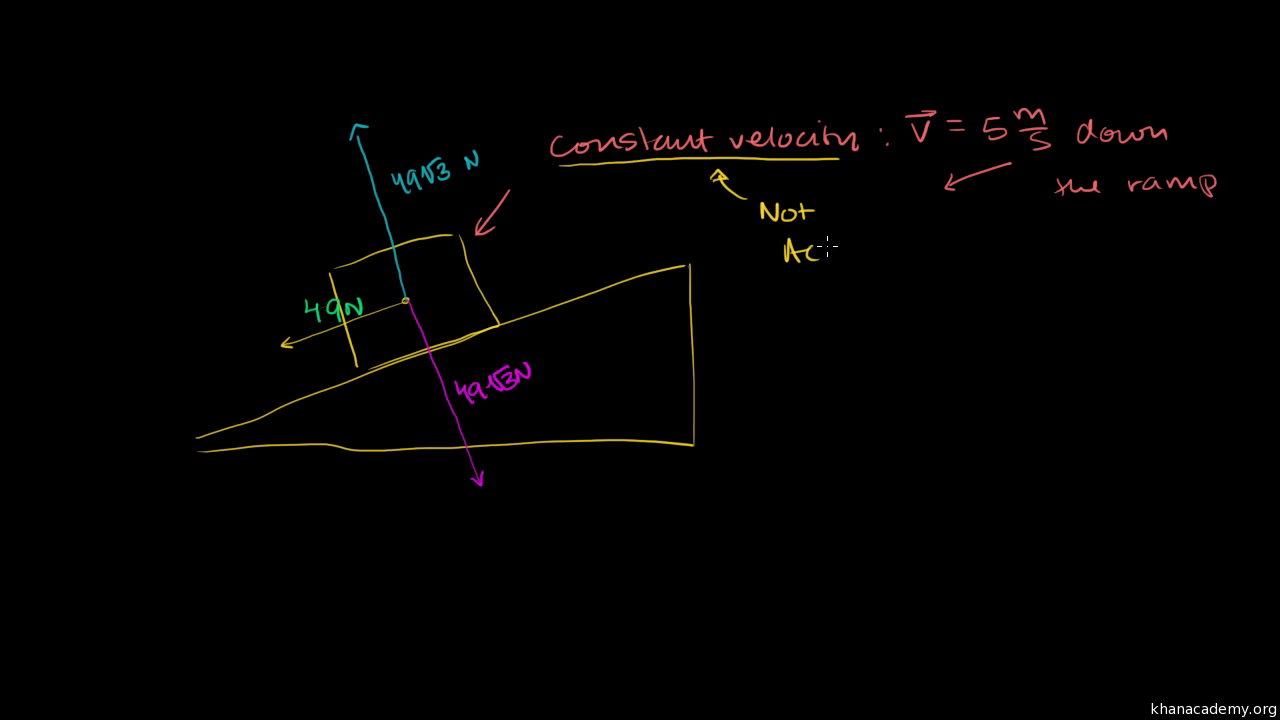
Practice: Newton's third law and free-body diagrams. This is the currently selected item. ... Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. Donate or volunteer ... A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting. Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... Using Free-Body Diagrams. Example: A sled During your winter break, you pull a rope attached to the sled with a force of 150 N at 25° above the horizontal. The mass of the sled-rope system is 80 kg, and there is negligible friction between the sled runners and the ice.
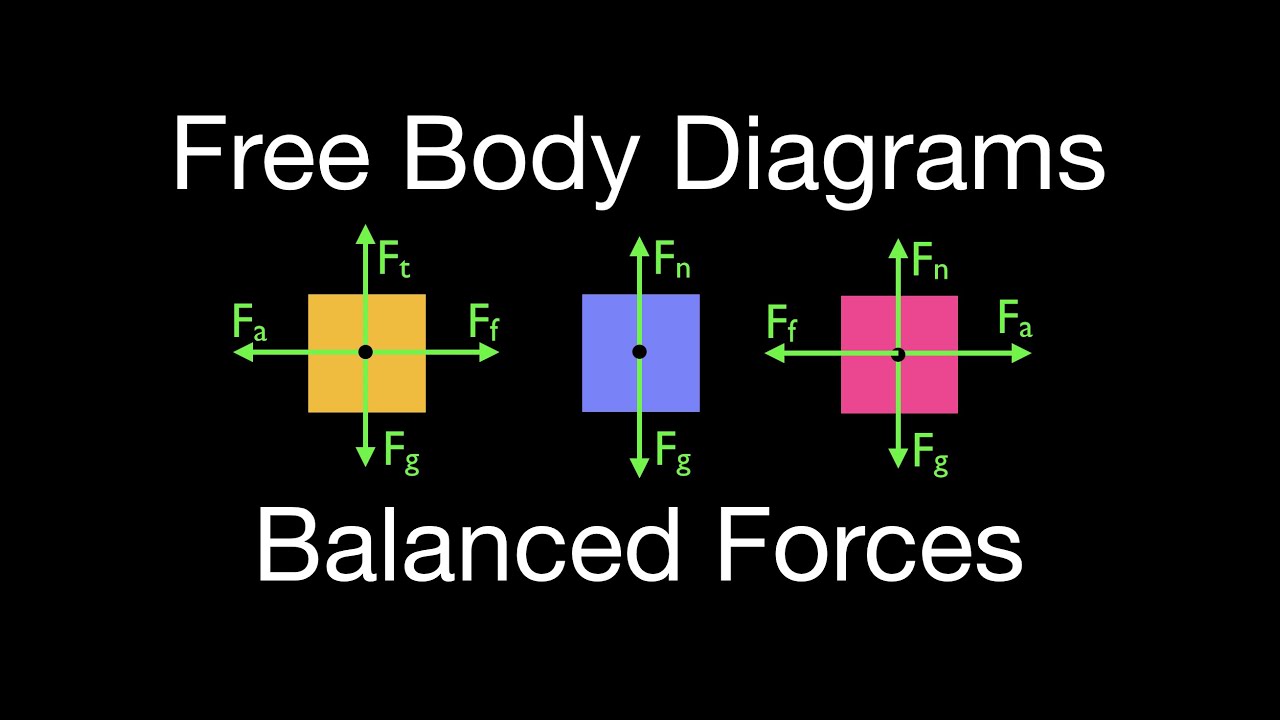
Introduction to free body diagrams Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization.
EQUILIBRIUM OF A PARTICLE, THE FREE-BODY DIAGRAM & COPLANAR FORCE SYSTEMS Today's Objectives: Students will be able to : In-Class Activities: a) Draw a free-body diagram (FBD), • Reading Quiz and, • Applications b) Apply equations of equilibrium to • What, Why, and How solve a 2-D problem.
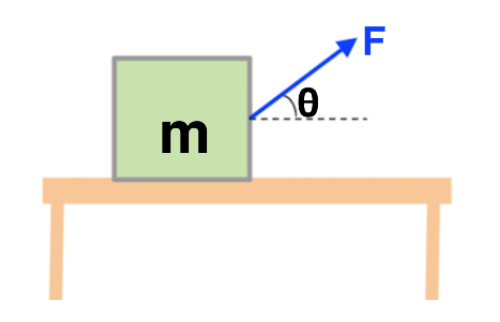
Sal explains how to draw free body diagrams when forces are applied at an angle. How to find horizontal and vertical components of an angled force using trig...
Keywords: free-body diagrams, self-constructed representations, problem solving, cognitive load, mechanics INTRODUCTION Today, there is a consensus in the scientific community that, in most contexts, individuals only can learn by putting mental efforts into the process of knowledge construction, whereby the
And to be clear, this five newtons, this is equal to the weight, the magnitude of the weight of the object. So that was pretty straightforward, the free body diagram for just the block. And it's really important to see that, because notice, in the free body diagram, all you see is the block. But now let's draw the free body diagram for the shelf.
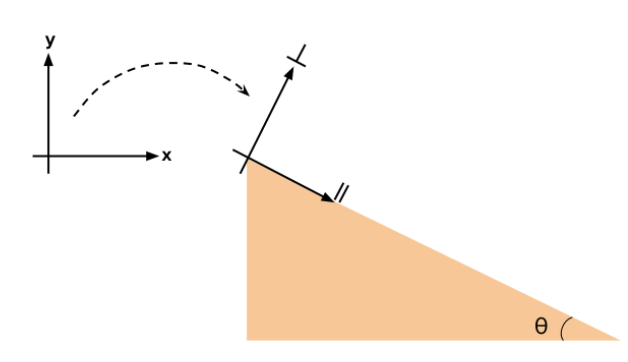
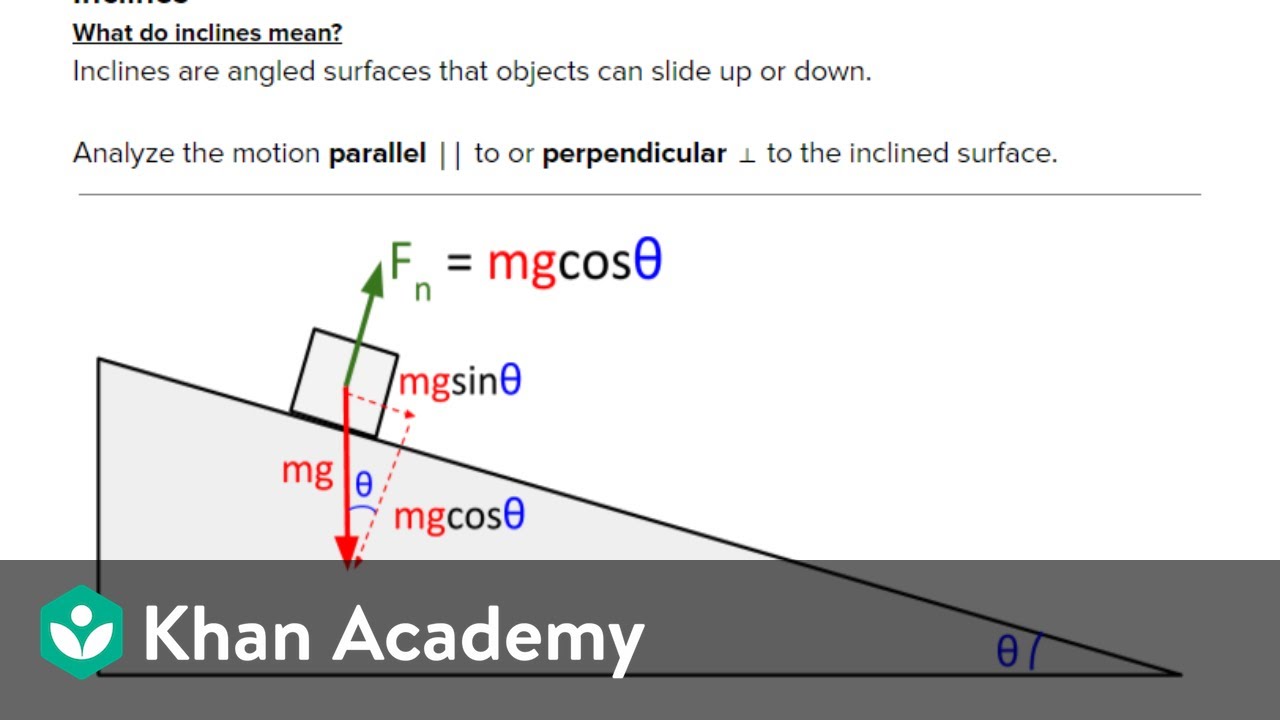
Figuring out the components of the force due to gravity that are parallel and perpendicular to the surface of an inclined plane. Created by Sal Khan.Watch th...
And to do it, I'm going to draw what's known as a free-body diagram to think about all of the forces. And the reason why it's called a free-body diagram is that we just focus on this one body. And we don't draw everything else around it, and we just draw the forces acting on it. And there's actually two typical ways of drawing a free-body diagram.
To proceed, we draw a free body diagram, showing the forces exerted by the spring and damper on the mass. Newton's law then states that . This is our equation of motion for s. Now, we check our list of solutions to differential equations, and see that we have a solution to:
Three times five is 15. Subtract, I get a two here, bring down the zero. Five goes into 20 four times. Four times five is 20, and it works out perfectly. So each of these five-fourths are 34 meters. 34 meters, 34 meters, 34 meters, 34 meters, and 34 meters.
Sal draws a free body diagram for a box held stationary against a wall with a force at an angle theta.View more lessons or practice this subject at https://w...
All About Vectors - website (physicsclassroom.com) - read Lessons 1 & 3 (see the Khan Academy video below for help with Lesson 3) Force Vectors (and the meaning of a vector's sense) - website (mit.edu) Free Body Diagrams (FBDs) - website (physicsclassroom.com) Drawing Free Body Diagrams - YouTube video1 and video2 (Bozeman Science). Solving for Forces Using a FBD (static case) - YouTube video ...






















Comments
Post a Comment