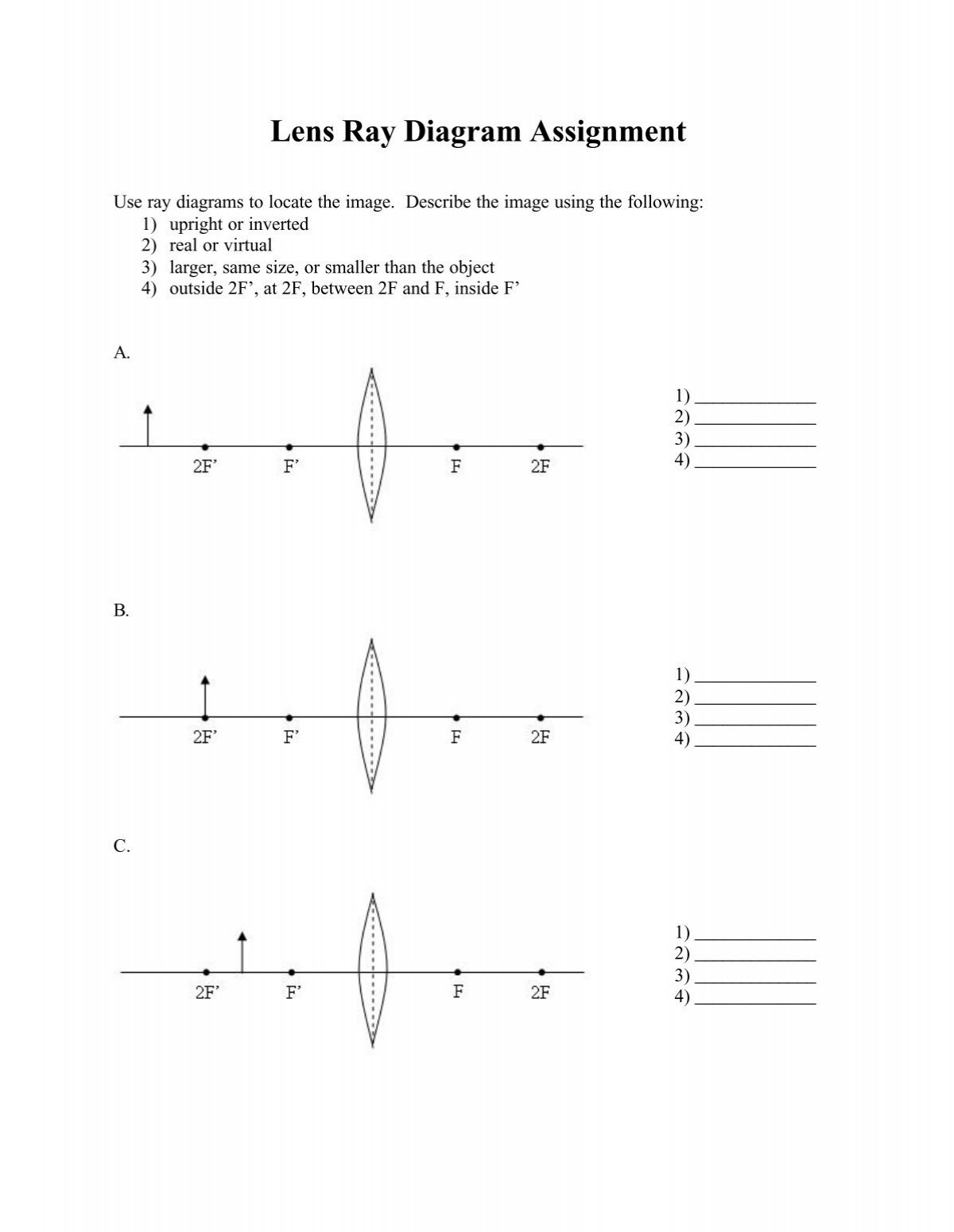
41 what is a ray diagram
This video covers:- How to draw ray diagrams for convex and concave lenses - How to comment on whether an image is real or virtual, upright or inverted, and ... A Ray Diagram is a way to represent how light is affected by the interface between to media. About Ray Diagrams. A Ray Diagram shows how light rays travel in ...
Our constitutional and legal system is remarkably ill-equipped to deal with an electoral crisis. Should we find ourselves in one, the system is more likely to exacerbate than defuse it. —Lawrence Douglas
What is a ray diagram
A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. There are a few important things to note: Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium). Answer: Taking two principal rays, the ray diagram below (courtesy of Wikipedia) would be sufficient as an answer. But for emphasis, please consider a third ray emanating from the top of the object (as the other two) and direct it to the POLE of the mirror. The ray would reflect off the mirror fo... A ray diagram is a specialized pictorial representation used to trace the path of light rays. The rules used for drawing ray diagrams are as follows. Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to FacebookShare to Pinterest Newer Post Older Post Home PDF FILE TO YOUR EMAIL IMMEDIATELY PURCHASE NOTES & PAPER SOLUTION. @ Rs. 50/- each (GST extra)
What is a ray diagram. Explain myopia with the help of a ray diagram. Medium. Answer. Myopia or short sightedness is the defect in which person is unable to focus far off objects clearly. This happens as the eye is unable to relax its eye lens enough to form the image on retina and the final image is formed in front of retina. This causes the person to see blurred ... Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual imagesmaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens. Ray diagrams for lenses Index Lens concepts HyperPhysics*****Light and Vision R Nave Go Back Cathode-ray-tube oscilloscopes have parallel metal plates inside them to deflect the electron beam. These plates are called the deflecting plates. Typically, they are squares 3.0 cm on a side and separated by 5.0 mm, with vacuum in between. Which geometric figures are drawn on the diagram? . Line segment C A Ray A C ∠ABC Circle C Ray B. Which geometric figures are drawn on the diagram? Check all that apply. Line segment C A Ray A C ∠ABC Circle C Ray B E ∠BCE Line segment A E. Categories CategoriesUncategorized. Leave a Reply Cancel reply.
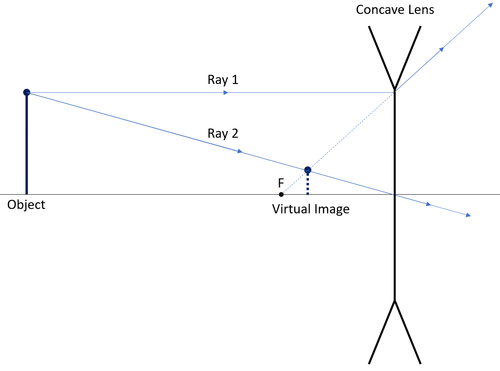
You need to enable JavaScript to run this app Ray diagrams It is important to be able to draw ray diagrams to show the refraction of a wave at a boundary. To draw a ray diagram: Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the... Ray Diagram for the Formation of a Virtual Image A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right. Observe that in this case the light rays diverge after reflecting off the mirror. When light rays diverge after reflection, a virtual image is formed. Ray diagrams A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: a straight line; with an arrowhead pointing in the...
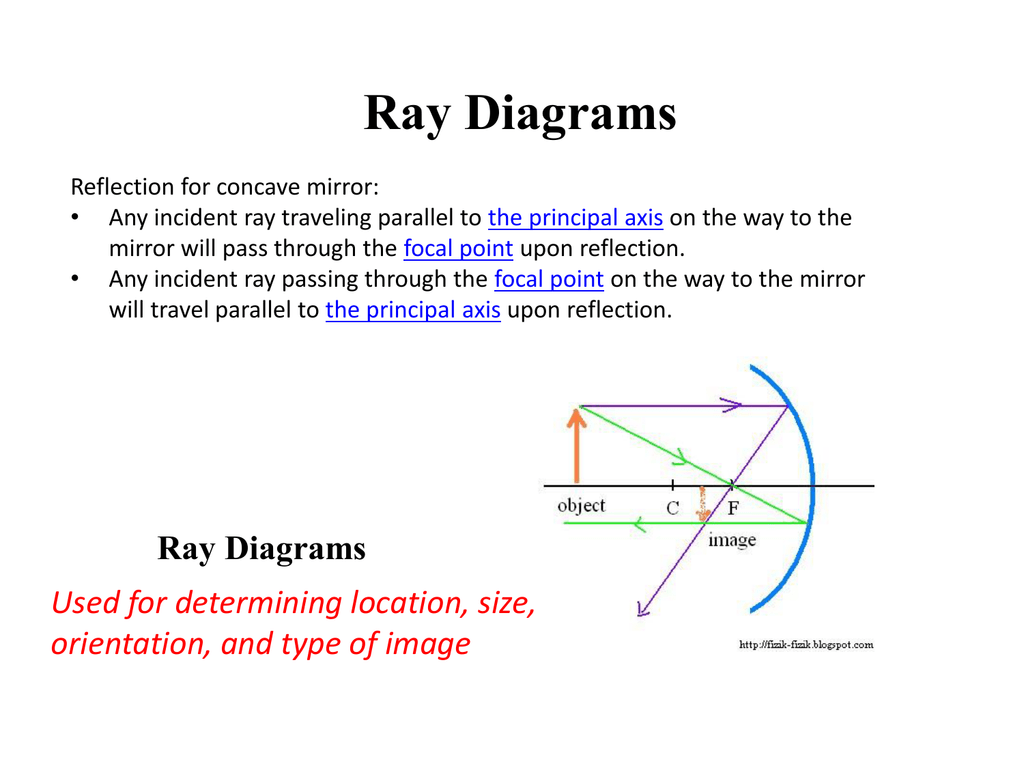
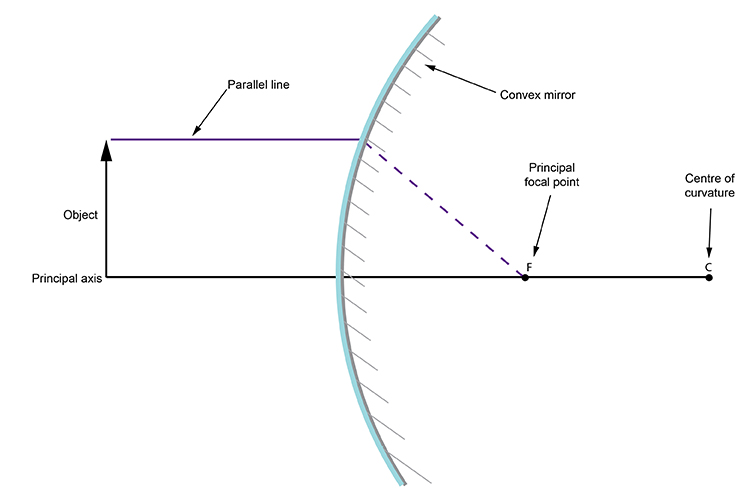
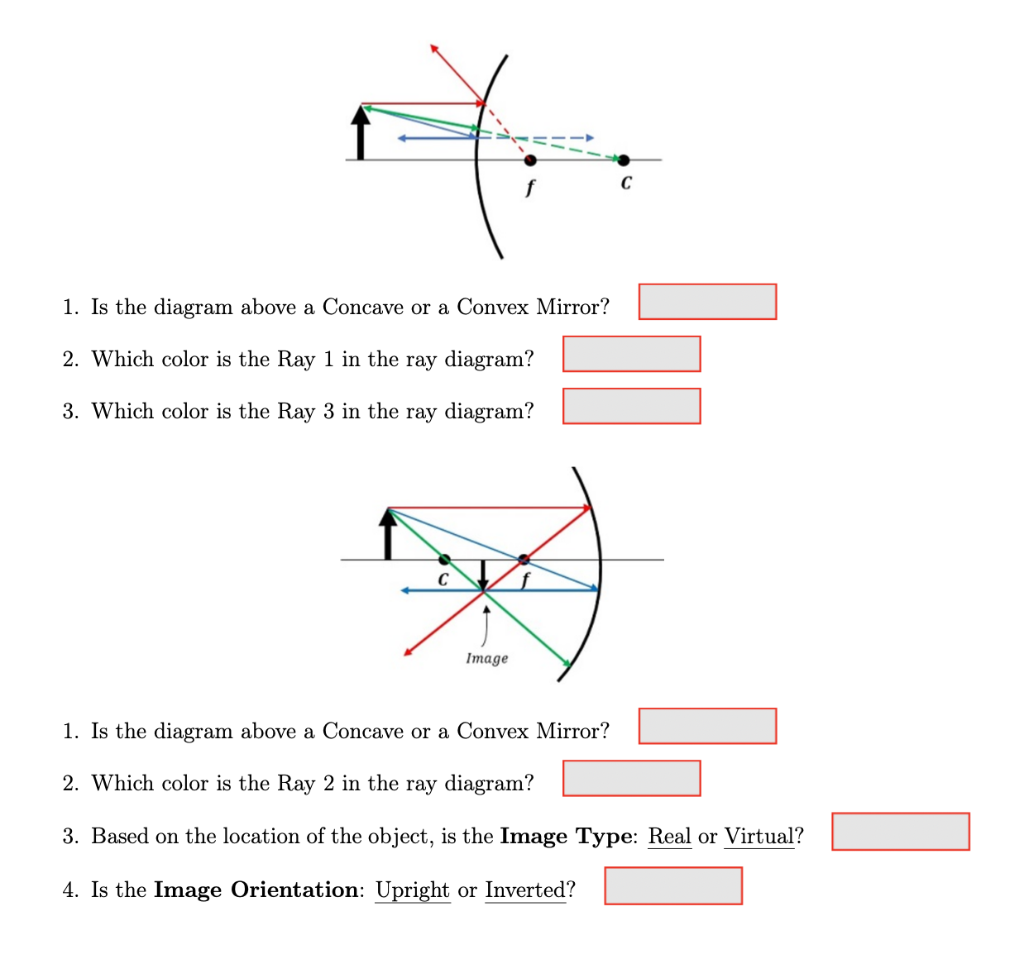
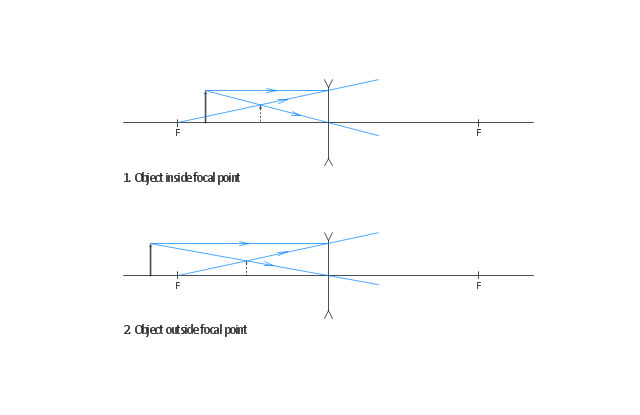
May 19, 2020 - The point of intersection demarcates the top of the image. The correct answer is A. As you may recall, an object within the focal distance of a converging lens will form an upright, virtual image on the same side of the lens as the object. Now you can draw ray diagrams to illustrate this point ... We first complete the given diagram with the angles of incidence and reflection as shown below and also labelling the incident and reflected rays. For the incident ray at A and the reflected ray at B to be parallel, angles i + r and i' + r' have to be supplementary. (geometry: parallel lines cut by a transversal). (a) Draw the ray diagram showing refraction of ray of light through a glass prism. Derive the expression for the refractive index of the material of prism in terms of the angle of prism A and angle of minimum deviation . (b) A ray of light PQ enters an isosceles right angled prism ABC of refractive index 1.5 as shown in figure. (i) Trace the path of the ray through the prism. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
A 1 4-year old student is not able to see clearly the questions written on the blackboard placed at a distance of 5 m from him. (a) Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. (b) With the help of labelled ray diagrams show how this defect can be corrected. (c) Name the type of lens used to correct this defect.
What is the cause of dispersion of white light through a glass prismDraw a ray diagram to show the path of light when two identical glass prisms are arranged...
Block Diagram of CRO. Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) consists a set of blocks. Those are vertical amplifier, delay line, trigger circuit, time base generator, horizontal amplifier, Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) & power supply. The block diagram of CRO is shown in below figure. The function of each block of CRO is mentioned below.
Explain ray diagrams. · Solution · A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as ...
This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging l...
The home entertainment experience has improved drastically over the years. Bigger televisions and more viewing options have revolutionized the way we screen movies and shows — so much so that some people rarely go to actual cinemas anymore....
What is a ray diagram? A ray diagram is used to determine the path followed by the light rays as they pass through the lens. The common components of a ray diagram for both convex and concave...
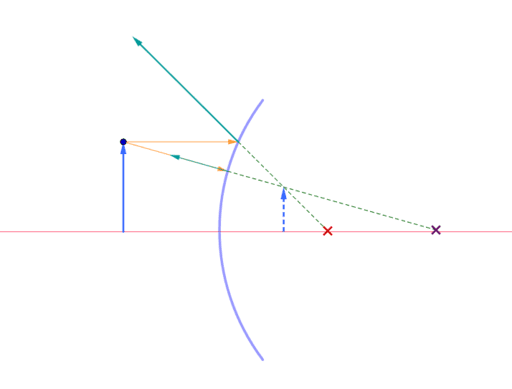
This section of Lesson 2 details and illustrates the procedure for drawing ray diagrams. Let's begin with the task of drawing a ray diagram to show how Suzie will be able to see the image of the green object arrowin the diagram below. For simplicity sake, we will suppose that Suzie is viewing the image with her left eye closed. Thus, we will focus on how light travels from the two extremities of the object arrow (the left and right side) to the mirror and finally to Suzie's right eye as she sights at the image. The four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. 1. Draw the image of the object. 2. Pick one extreme on the image of the object and draw the reflected ray that will travel to the eye as it sights at this point. 3. Draw the incident ray for light traveling from the corresponding extreme on the object to the mirror. 4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for all other extremities on the object.
Constructing a ray diagram. Demonstrate the shadow to the class and pose the key question: Teacher: How can we draw a diagram to show how the shadow is formed on the screen? Now turn the class's attention to the screen. Here is a possible commentary to go alongside whole class use of the animation.
in this video we're gonna take ... video and try to draw a ray diagram yourself for this all right for me it's very easy to do this on the app first of all notice the paddle Ray's gonna look exactly the same the only thing I have to do is get rid of this part over here but ...
13. maj 2020 ... A ray diagram is defined as the representation of the paths taken by the light when the light is passed through one point to the other.
Ray diagrams · A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. · In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: · Remember to use ...
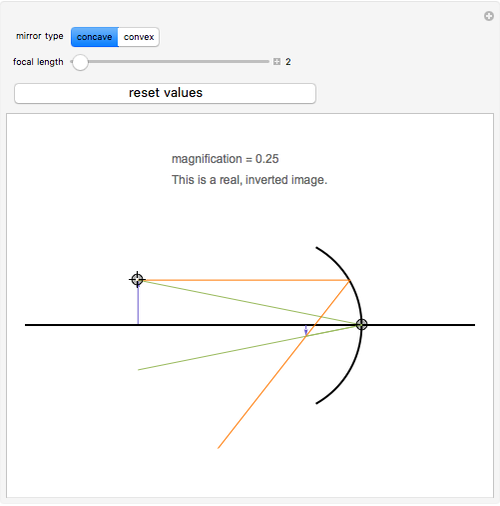
Ray diagrams are drawings that use simple geometry to locate an image formed by a mirror. In order to draw a ray diagram, first sketch the situation; draw the location and arrangement of the mirror...
Ray diagram • A ray diagram is a representation of structural formula. It provides information such as speed in each stage, the transmission ratio in each stage, The total number of speeds and its values. • As seen in fig. (a) the maxi speed and minimum speed both are higher for shaft. This requires smaller size of shafts due to reduced torque.
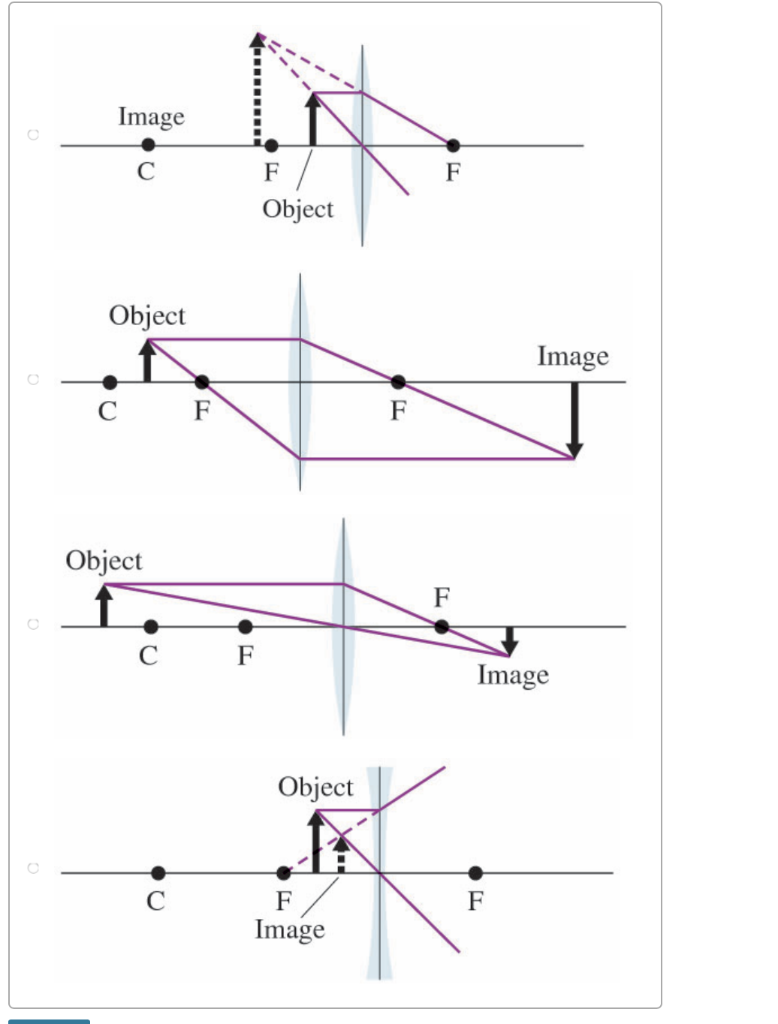
Once through the lens, the ray should pass through the principal focus. Draw a ray which passes from the object through the centre of the lens. Some ray diagrams may also show a third ray. The type of image formed by a convex lens depends on the lens used and the distance from the object to the lens. Cameras and eyes contain convex lenses.
A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens, passing through the principal focal point beyond the lens. What is a lens ray diagram?
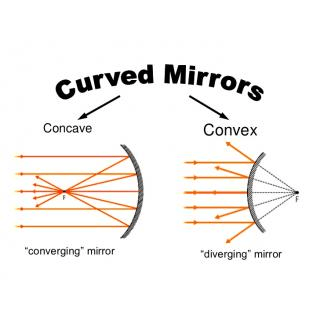
Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracing in that rays parallel to the optic axis and through the focal point are used. A third useful ray is that through the center of curvature since it is normal to the mirror and retraces its path backward · A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The ...
The Racheal Ray Show is popular for its fun host and tasty, approachable recipes. The next time you’re planning out a menu, consider adding one of her popular dishes to your weeknight rotation. Or surprise your family and friends with a spe...
121 - Ray Diagram - MirrorsIn this video Paul Andersen explains how ray diagrams can be used to determine the size and location of a reflected image. Ray di...
One of the distinctive and interesting features of teaching and learning about light is the way in which ideas and explanations are represented with ray diagrams. Rather than just talking through an explanation for some effect or other, you'll often find yourself constructing and referring ...
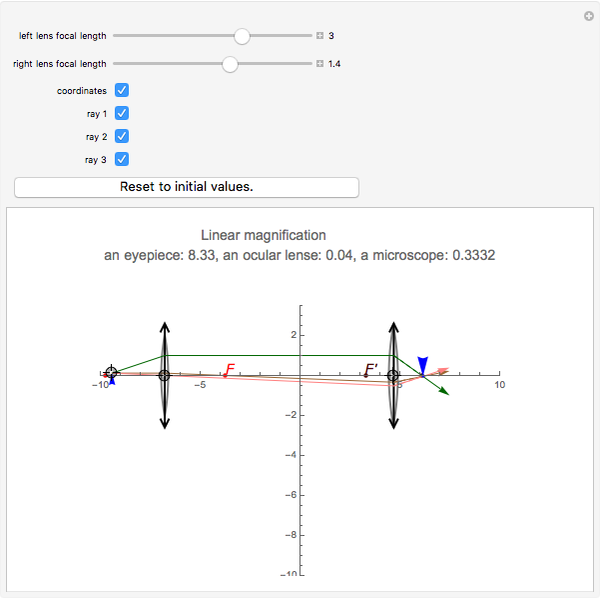
Ray Diagrams. Jonathan is a published author and recently completed a book on physics and applied mathematics. All lenses and mirrors can use ray diagrams to find images. There are three principal rays. The first principal ray occurs when the light comes in parallel to the principle axis, it goes out through the focus.
Main Problem With Spot Diagrams • The main problem is that spots in the spot diagram don't convey intensity – A ray intersection point in the diagram does not tell the intensity at that point 0.000,0.000 DG 0.00, 0.00 0.000,10.00 DG 0.00, 0.71 0.000,14.00 DG 0.00, 1.00 FIELD POSITION DEFOCUSING 0.00000 Double Gauss - U.S. Patent 2,532,751 ...
Rachael Ray show star: best way to lose weight and get fit. Rachael Ray shares how she loves going to the gym every morning Women's Health may earn commission from the links on this page, but we only feature products we believe in. Why trus...
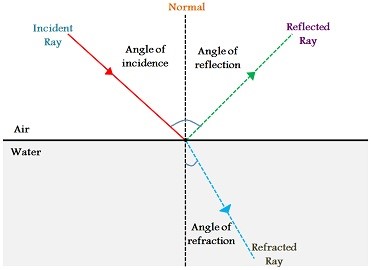
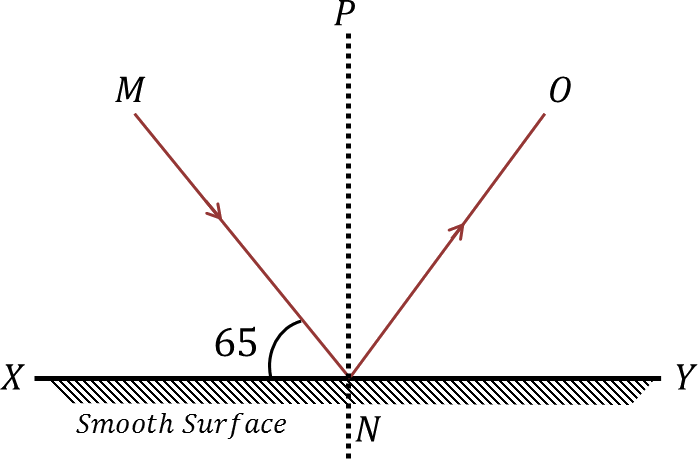
Q. The angle between the incident ray and the normal. (X on the diagram) answer choices. Angle of X-Ray. Angle of Reflection. Angle of Incidence. Angle of Normal.
Angle of X-Ray
.How to Draw a Ray Diagram for an Object in Front of a Concave Mirror. Step 1: Draw two incident rays departing from the top of the object and reaching the mirror in different directions. Step 2 ...
A ray diagram is a tool used by physicists to explain or predict the behaviour of beams of light as they pass through objects such as glass blocks or lenses. When ray diagrams are first introduced, students not surprisingly often assume that they show the world as it really is.
Question 9. SURVEY. 60 seconds. Q. When an object is placed on the focal point in front of a convex lens, the image produced is ___. answer choices. real, reduced, and inverted. real, magnified, and inverted.
A ray diagram is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object. On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. What is focal length in a ray diagram? 1a A simple ray diagram for a converging convex lens.
A ray diagram shows the path that the ray of light follows while passing through the lens. When the light rays go through the convex lens, the observer notices a change in its path, and the convex lens ray diagram describes this change. Based on the position of the object, the formation of the image can differ
Given rays of light incident on spherical mirrors, let's practice drawing the reflected rays.
The object is the source of the ... image is formed by the reflected rays. Based on the interaction of light, the images are classified as either a real image or a virtual image. A real image occurs when the light rays actually intersect while virtual images occur due to the apparent divergence of light rays from a point. Ray diagrams help us trace ...
A grid of points is defined at the entrance or exit pupil. of an optical system and rays are traced from the object point. through the grid points, through the observation plane.
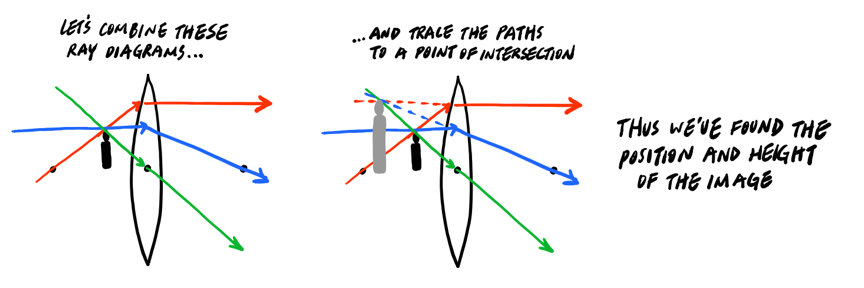
Ray Diagram for Object Located at the Focal Point. Thus far we have seen via ray diagrams that a real image is produced when an object is located more than one focal length from a converging lens; and a virtual image is formed when an object is located less than one focal length from a converging lens (i.e., in front of F). But what happens when the object is located at F?
Rule 2 - Ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis. For a convex lens, we see that ray passing through focus on left becomes parallel to principal axis after refraction. For a concave lens , since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis.
ray diagram. noun. 1 A diagram showing straight lines radiating from a central object. 2 Physics A diagram showing the paths of light rays through an optical system; also in extended use. Origin. 1950s. Word of the day. hoon / huːn / noun. See definitions & examples.
January 1, 1995 - The lens drawn is a particular kind of lens called a converging lens. It has the property that light coming from very far away will be focused down to a point, called the focal point. We draw this as: This is our first ray diagram. The solid lines represent rays of light.
Drawing the ray diagram: Using a scale of 1: 5, we get v = - 2 cm, f = - 3 cm. We draw the ray diagram as follows: (i) Draw the principal axis (a horizontal line). (ii) Draw a convex lens, keeping principal centre (C) on the principal axis. (iii) Mark points F and B on the left side of lens at a distance of 3 cm and 2 cm respectively.
Give Mr. H just 6 minutes to explain what a ray diagram is and to demonstrate how to construct a ray diagram for a point object and an arrow object. Examples...
A ray diagram is a specialized pictorial representation used to trace the path of light rays. The rules used for drawing ray diagrams are as follows. Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to FacebookShare to Pinterest Newer Post Older Post Home PDF FILE TO YOUR EMAIL IMMEDIATELY PURCHASE NOTES & PAPER SOLUTION. @ Rs. 50/- each (GST extra)
Answer: Taking two principal rays, the ray diagram below (courtesy of Wikipedia) would be sufficient as an answer. But for emphasis, please consider a third ray emanating from the top of the object (as the other two) and direct it to the POLE of the mirror. The ray would reflect off the mirror fo...
A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. There are a few important things to note: Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium).




















Comments
Post a Comment