43 centripetal force free body diagram
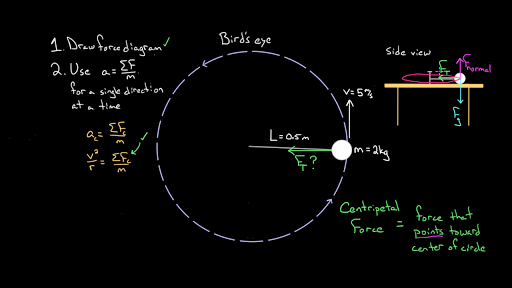
Solving for Centripetal Force using a Free Body Diagram ... PhysicsVelocityRadiusWeightCentripetal Force Chantelle W. asked • 03/07/16 Solving for Centripetal Force using a Free Body Diagram A 70 kg student is riding a roller coaster and is at the top of the vertical loop. The loop has a radius of 16 m, and the car's velocity at the top is 12 m/s. What is the student's apparent weight at that moment? Students' Common Mistakes in Making Free-Body Diagrams ... Mistake 2: "Centripetal Force" was Added to the Free-Body Diagram. Centripetal force is a tricky item when it comes to free-body diagram. The short answer is - do not add centripetal force in a free-body diagram because it is not one of those contributing forces like gravity, normal reaction force, tension force, etc. It is simply a convenient way of describing the effect o resultant force.
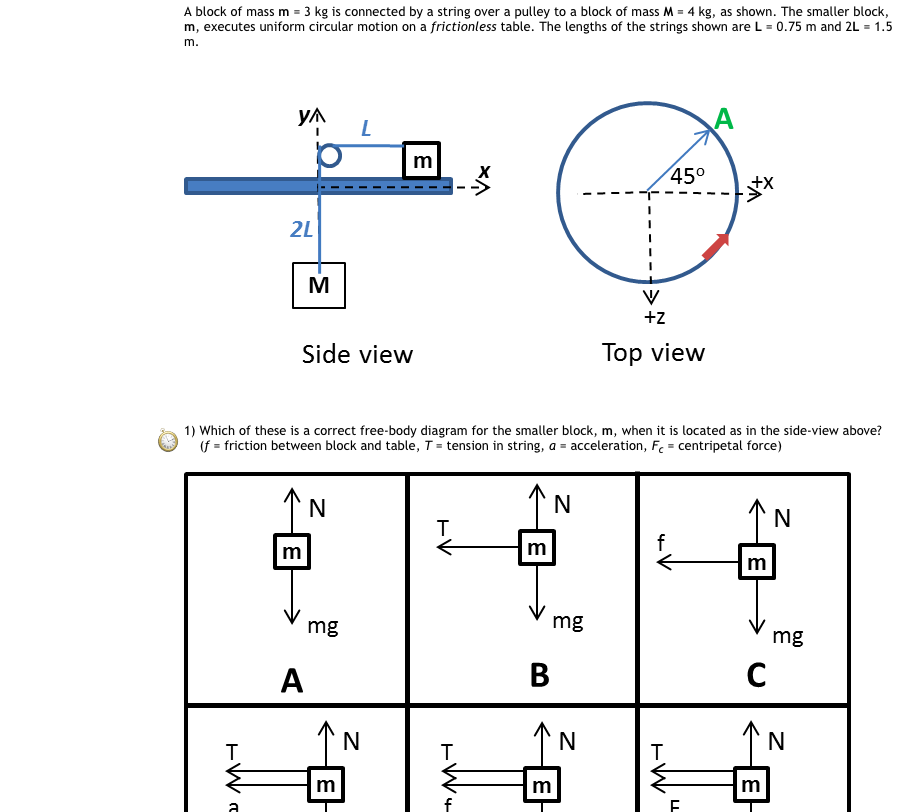
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton's third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution Significance →A 21 A → 21 is the action force of block 2 on block 1. →A 12 A → 12 is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton's Laws. Example

Centripetal force free body diagram
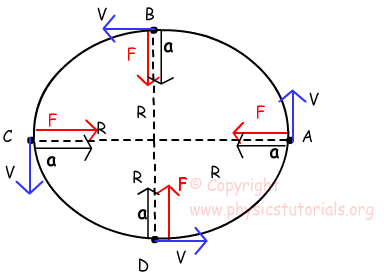
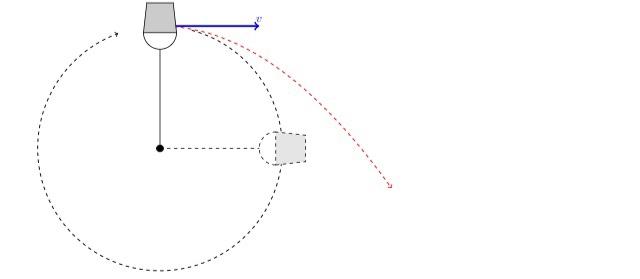
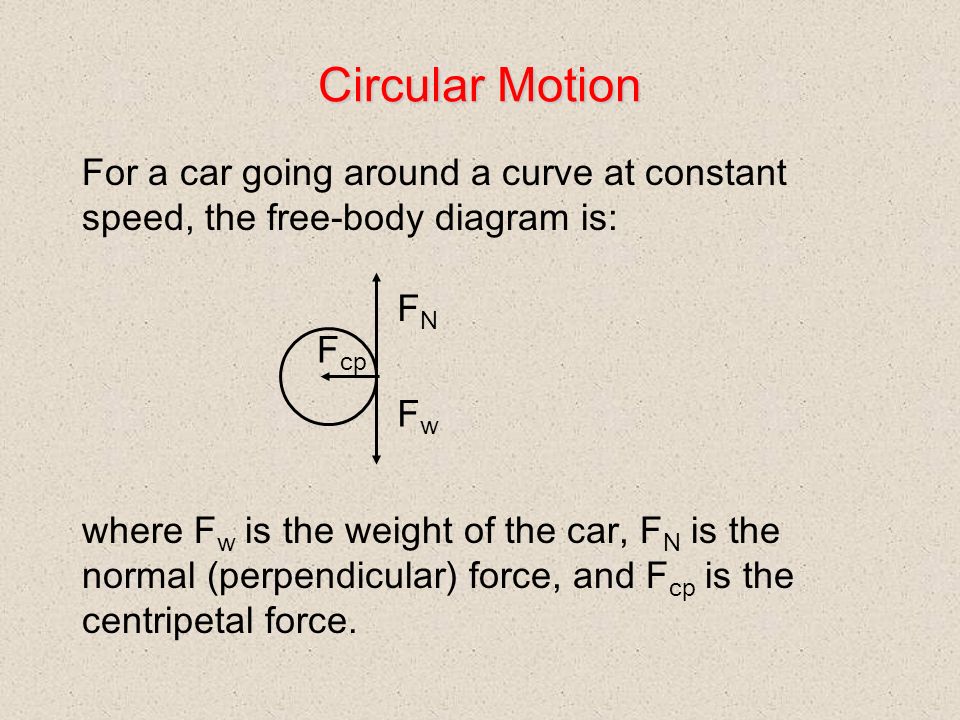
Physics 1120: Newton's Laws Solutions 6. In the diagram below, an object travels over a hill, down a valley, and around the inside of a loopthe loop. At each of the specified points draw a free body diagram indicating the directions of the normal force, the weight, and the centripetal acceleration if it exists. Centripetal Force Introduction and Demonstration Learn why a centripetal force exists, three important things to remember about centripetal force, and drawing free body diagrams for objects moving in circles. This is an AP Physics 1 topic. Content Times: 0:01 Newton's Second Law for Centripetal Force. 1:10 Three things to remember about Centripetal Force. 2:41 Drawing a free body diagram. 6.3 Centripetal Force - University Physics Volume 1 (Figure) shows a free-body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve. If the angle is ideal for the speed and radius, then the net external force equals the necessary centripetal force. The only two external forces acting on the car are its weight and the normal force of the road
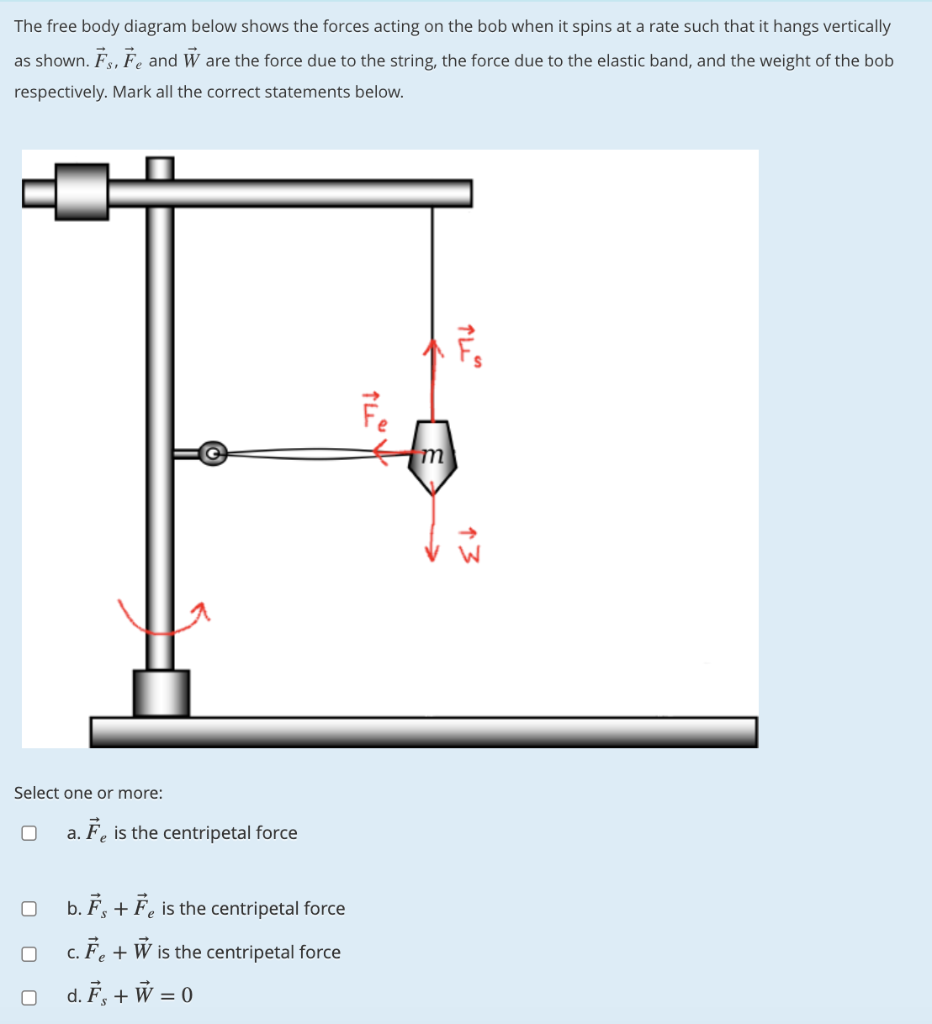
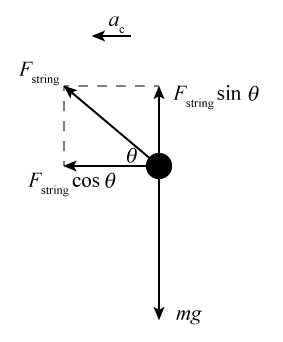
Centripetal force free body diagram. Why isn't centrifugal force drawn on a free body diagram ... When a free body diagram of a ball being swung in a circle is drawn ( example ), only tension and weight are drawn on it. I understand that the centripetal force equals tension plus weight at the top of the circle, and tension minus weight at the bottom of it, but there must also always be an equal centrifugal force because of Newton's 3rd Law. 6.3 Centripetal Force - College Physics: OpenStax Any net force causing uniform circular motion is called a centripetal force. The direction of a centripetal force is toward the center of curvature, the same as the direction of centripetal acceleration. ... Figure 3 shows a free body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve. If the angle[latex]\boldsymbol{\theta}[/latex]is ideal for ... Why isn't centripetal force shown on the free-body diagram ... What is called the centripetal force is the horizontal component of the tension on the string, given as T sin (A). It is not a force by itself, but is just a component of the tension T. To be able to revolve in a circle with radius R, there must be a force on the bob, equal to it mass times its velocity squared over R. courses.lumenlearning.com › 6-3-centripetal-forceCentripetal Force | Physics - Lumen Learning Figure 1. The frictional force supplies the centripetal force and is numerically equal to it. Centripetal force is perpendicular to velocity and causes uniform circular motion. The larger the F c, the smaller the radius of curvature r and the sharper the curve. The second curve has the same v, but a larger F c produces a smaller r′.
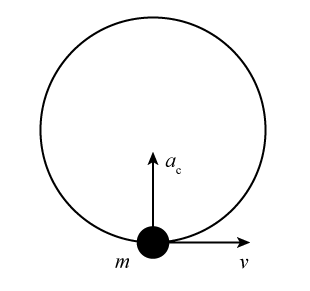
Uniform circular motion - Boston University You do NOT put a centripetal force on a free-body diagram for the same reason that ma does not appear on a free body diagram; F = ma is the net force, and the net force happens to have the special form when we're dealing with uniform circular motion. Understanding centripetal force and free body diagram ... Never put 'centripetal force' on a free body diagram. There are only 2 forces acting on the body: The weight, mg, and the force of the earth pushing up, the 'reaction force'. so there is no reaction force to mv^2/r? Don't think of mv^2/r as a separate force; think of it as applying Newton's 2nd law in the case of centripetal acceleration. Centripetal Force and Centrifugal Force - Definition ... According to the centripetal force definition, Centripetal force is the force acting on an object in curvilinear motion directed toward the axis of rotation or centre of curvature. The unit of centripetal force is newton. The centripetal force is always directed perpendicular to the direction of the object's displacement. Why don't we consider centripetal force while making FBD ... The centripetal force is not a new force. It is just a name we give to whichever force that pulls centripetally (towards the centre in circular motion). In your case there is a component from the normal force which pulls centripetally (horizontally leftwards). So that is called the centripetal force. From the non-inertial frame
Physics Help: Centripetal Force Free Body Diagrams Part 7 ... simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website. Lesson 7: Forces and Free Body Diagrams - Quantum Tunneling Create an applied force and see the resulting friction force and total force acting on the cabinet. Charts show the forces, position, velocity, and acceleration vs. time. View a Free Body Diagram of all the forces (including gravitational and normal forces). Click to Run In the playlist below, video: Will show you how to draw free body diagrams. OpenStax College Physics Solution, Chapter 6, Problem 29 ... (Hint: The arm supplies centripetal force and supports the weight of the cage. Draw a free body diagram of the forces to see what the angle $\theta$ should be.) Question Image. Figure 6.37 NASA centrifuge used to subject trainees to accelerations similar to those experienced in rocket launches and reentries. (credit: NASA) (b) Rider in cage ... Uniform circular motion - Home | Boston University Physics There is no such thing, and, in my opinion, you should never put a centripetal force on a free-body diagram. When an object is experiencing uniform circular motion there is definitely a net force directed toward the center of the circle, but this force comes from one or more of the standard forces we've discussed already.
Forces and Free-Body Diagrams for Circular Motion Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion The Forces in Circles Concept Builder provides learners with the challenge of identifying the free-body diagrams for situations involving the motion of objects in circles. Learners are presented with a short verbal description of an object's motion.
Centripetal Force Sample Problem Using Free Body Diagrams ... AHEAD and click on this site...it wont hurt.Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website
PDF Free Body Diagrams - Singapore University of Technology ... examples of free body diagrams with an opportunity to practice, examples of situations in which diagrams have been drawn incorrectly (and corrections for them), a &nal segment that draws ... it was decided that centripetal force could not be treated properly in this video. %e original script and slides for this section of the video
PDF 5. Forces and Free-Body Diagrams Forces and Free-Body Diagrams A) Overview ... examples of uniform circular motion and therefore we know that each orbiting body experiences a centripetal acceleration. Therefore, in Newton's framework, there must be a real force being exerted on the orbiting body that is responsible for this acceleration. Newton proposed that this force was a ...
PDF Physics Kinematics, Projectile Motion, Free-Body Diagrams ... Free-Body Diagram Example Problem 2 A car with a mass of 1050 [kg] travels around a curve of radius 300 [m] banked at a 14˚ angle. Find the maximum speed the car can take this curve without assistance from friction. Find the centripetal force on the car.
diagramweb.net › free-body-diagram-centripetalFree Body Diagram Centripetal Force Jan 27, 2019 · Figure 3 shows a free body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve.It is the friction force that supplies the centripetal force requirement for the car to move in a horizontal circle. Without friction, the car would turn its wheels but would not move in a circle (as is the case on an icy surface). This analysis leads to the free-body diagram shown at the right. I having difficulty in explaining to my son the free-body diagram for following problem: A child flies a toy sphere ...
Centripetal Force - Physics 298 careful. The centripetal force is NOTa force to be included on a free body diagram. Rather, the net force towards the center of the circle should be set equal to Fc(= mv2/r = ma). Combining your knowledge of frictional forces with centripetal force
schematron.org › free-body-diagram-centripetalFree Body Diagram Centripetal Force - schematron.org Apr 20, 2019 · The correct free-body diagram is diagram 3, which shows only the force of gravity applied by the Sun on the Earth. The word “centripetal” means “directed toward the center.”. When an object experiences uniform circular motion, the object has a centripetal acceleration directed toward the center of the circle.
Pseudo Force - BYJUS So if C draws a free body diagram of B, it will have a net force that gives acceleration. ... But if there is radial acceleration in a body with respect to a frame then in that frame centripetal force will not be equal to centrifugal force. Is work done by these forces to be considered for work-energy theorem?
Amusement Park Physics - Physics Classroom Once more the F norm must provide sufficient force to produce the required inward or centripetal net force. Earlier in Lesson 2, the use of Newton's second law and free-body diagrams to solve circular motion diagrams was illustrated. It was emphasized at that time that any given physical situation could be analyzed in terms of the individual ...
Centripetal Force - Pendulum Form - CBakken The forces at the bottom are shown here in a free-body diagram. The two forces at the bottom are co-linear, with the upward tension force T being larger than the downward weight, mg, by the required centripetal force. In your experiment, you will compare the measured tension force with one calculated based on the motion. Figure 1.
Understanding centripetal force and free body diagram ... mv^2/r is the net force towards the center on something that is executing circular motion. The forces acting on the body will be gravity and the normal force. Oct 25, 2011 #68 jsmith613 614 0 ok so if 20 kg moves at a speed of 10 m/s and a radius of 3m then the NET force i need (Fc) is 666.666N
6.3 Centripetal Force - University Physics Volume 1 (Figure) shows a free-body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve. If the angle is ideal for the speed and radius, then the net external force equals the necessary centripetal force. The only two external forces acting on the car are its weight and the normal force of the road
Centripetal Force Introduction and Demonstration Learn why a centripetal force exists, three important things to remember about centripetal force, and drawing free body diagrams for objects moving in circles. This is an AP Physics 1 topic. Content Times: 0:01 Newton's Second Law for Centripetal Force. 1:10 Three things to remember about Centripetal Force. 2:41 Drawing a free body diagram.
Physics 1120: Newton's Laws Solutions 6. In the diagram below, an object travels over a hill, down a valley, and around the inside of a loopthe loop. At each of the specified points draw a free body diagram indicating the directions of the normal force, the weight, and the centripetal acceleration if it exists.










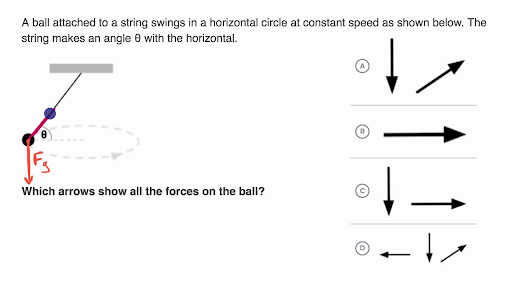
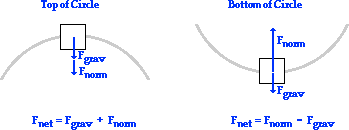
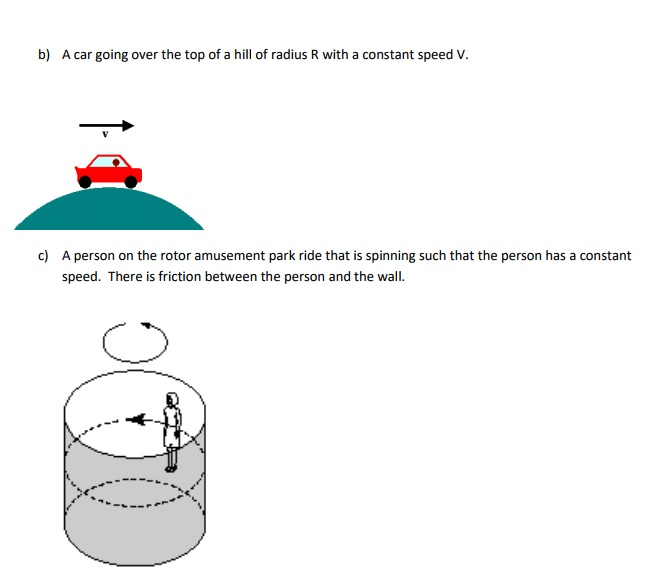
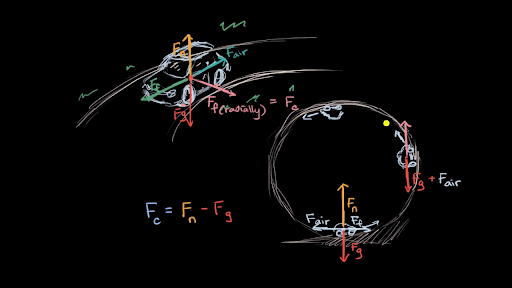



Comments
Post a Comment